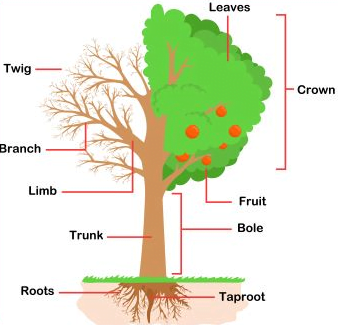
From the tree outside your house to the mosses and tussock grass in Antarctica, you will find plants everywhere. To date, over 300,000 plant species have been identified. However, botanists believe that there are still tens of thousands of unidentified species yet to be discovered. Humans rely on plants. Directly or indirectly, plants provide food, shelter, clothing as well as many other necessities. read on to find out the uses of plants in more detail.
Practical uses of plants
Plants are used as food

Plants make starches and sugar for their own growth. These starches are also rich in the fundamental nutrients required by humans. Hence, we consume the stored starch as food.
Firstly, humans consume cereals or food grains. Cereals are seeds of plants from the grass family. We use cereals like rice, wheat, maize, millet, barley, gram, jowar, etc to prepare a variety of dishes. Seeds of some other plants find uses as pulses. For example, pea, green gram, yellow gram, lentil etc. Some seeds are oily. Therefore, we extract the oil from the seeds for our daily use. Some oily seeds include coconut, peanut, sesame etc. People use some seeds like almonds, raisins, chestnuts etc as dry fruits.
Apart from the seeds, plants store starch in the roots and fruit as well. Humans consume roots of radish, carrot, beet etc. We also eat the fruits produced. For example, mango, apple, orange, grapes etc. Furthermore, fruits are generally eaten raw and are rich in minerals and vitamins.
Some plants also give us vegetables. Potato, onion, tomato, ladyfinger, bean, cauliflower, pumpkin etc. are some of the vegetables we consume. Vegetables are rich in iron, vitamins as well as other minerals.
Lastly, we also obtain spices from plants. People have used spices in cooking for ages to make the dish taste better. They even help preserve the food for longer. Some examples are pepper, cumin, ginger, garlic, cardamom, thyme, clove, rosemary, cinnamon, etc. Cash crops like tea and coffee are also staple beverages in any person’s diet. In some parts of the world, especially Asia, seaweeds, a form of algae, are an essential component of a person’s diet.
Plants are used in the industries
Plants grown as industrial crops are required for manufacturing a wide variety of products. Nonfood products include natural dyes, pigments, resins, alkaloids, waxes, tannins and cork. Flowers and leaves are used to produce rich natural dyes to colour clothes. Structural materials, as well as fibres from plants, are used to manufacture clothing as well as in construction. For example, wood is not only used to make buildings, we also use it to create furniture, boats as well as musical instruments. Fibres from the cotton, flax, ramie plant as well as synthetic fibres like rayon (derived from plant cellulose) are spun into threads and used to sew clothes to cover the human body.
Paper is made from trees and plants

Another essential product obtained from lant is paper. Used in daily life, paper is over 4,500 years old. The ancient Egyptians were the first to prepare paper from the fibrous stems of plants like papyrus. In AD 100, the Chinese invented the method of manufacturing paper that is still used to this day. The collected plant fibres are placed in water to make pulp. The water is removed and the pulp is pressed and dried to yield a thin sheet of paper.
Some plants help us make shelters

The shelter is crucial for human survival. In most parts of the world, shelter is made out of wood. Furniture is also commonly crafted from wood. Walls are often covered with paper or paints.
Plants are used in cosmetic industry

Plants are also used in the cosmetic and beauty industry. They are used in the manufacture of different products like body scrubs, shampoo and conditioners among others. In addition, crushed flowers and fruits can be used to make products like blush, lipstick as well as a lip balm that are used to beautify the face. Flowers of certain plants are also used to make perfumes. Some examples include rose, jasmine, lavender etc. The essential oils present in them have a rich and alluring scent. Furthermore, flowers are also used to make garlands and for other decorative purposes.
Plants are used as fuel
Coal, petroleum and natural gas are fuels used daily for heating and cooking. Each originated from plants and other organisms that lived on the planet a thousand years ago. After the organisms died, their remains were buried deep underground, where pressure and heat converted them to fossil fuels. Peat, which is formed from partially decayed plant material buried in wetlands, is also commonly used as fuel.
Wood is still burned for heat in many cold countries, and charcoal, formed from incompletely burned wood, is used in many tropical countries where other fuels are unavailable or expensive. Additionally, charcoal is also popular for outdoor cooking.
Plants are used in medicine

Through the ages, people have discovered that certain plants could relieve their aches and pains. In fact, most medicine men, as well as physicians in ancient times, were experts on plants. The study of botany in America as well as Europe has its beginnings in medicine. Now, hundreds of medicines are derived from different parts of a plant. This includes both traditional medicines used in Ayurveda as well as chemical substances purified from plants for use in modern medicine. The different plants in medicine include,
Use of medicinal plants today
Many medicinal plants that were discovered hundreds of years ago are still in use today. For example, Native Americans chewed on the leaves of willows to lessen aches and pains. These leaves have salicylic acid, a compound that is very similar to aspirin, an analgesic. Foxglove leaves produce digitalis, which is used to treat heart disease and quinine, produced by the bark of the cinchona tree, has been used to combat malaria for ages.
Medicinal substances are still being discovered in plants. For example, Vincristine, which has proved to be effective in the treatment of leukaemia in children. It is a compound produced by the periwinkle plant. The periwinkle is commonly cultivated in gardens across the world.
However, not all drugs produced by plants are beneficial. Some are poisons or habit-forming narcotics. For example, peyote, which is derived from a cactus, as well as opium, which comes from a poppy.
Medicinal plants are used as chemicals
Pesticides derived from plants include rotenone, nicotine, pyrethrins and strychnine. Plants such as opium poppy, tobacco, cannabis, and coca yield psychotropic chemicals. Poisons from plants include ricin, atropine and hemlock.
Medicinal plants are used in science

Plants are commonly used in basic biological research since the old ages. Some scientific discoveries that came from studying plants include,
- In genetics, Gregor Mendel observed the breeding of pea flowers to derive the basic laws governing inheritance.
- Examination of chromosomes in corn allowed Barbara McClintock to demonstrate their connection to inherited traits.
- The plant Arabidopsis thaliana is used as a model organism to understand how genes regulate the growth and development of plant systems.
- Scientific advances in genetic engineering led to the development of disease and drought-resistant crops, which are greatly beneficial to the farmers. Other modifications include a decrease in the use of harmful pesticides by creating insect-resistant as well as herbicide-tolerant varieties of crops.
Medicinal plants are used as living structures
The ability of trees to graft is exploited by tree shaping to make living root bridges such as the ones in Meghalaya and Nagaland in India. A similar one is also found on the islands of Java and Sumatra in Indonesia. Furthermore, aerial roots of the rubber fig trees are used to create suspension bridges across mountain streams.
List of Common medicinal plants
| Hindi Name | English Name | Botanical Name | Uses |
| Adusa/Vasaka | Malabar Nut | Adhatoda vasica Nees Pennel | Cough, Asthma, Bronchitis |
| Ananas | Pineapple | Ananas comosus Pennel | Sore Throat, Diabetes, Heart Disease, Obesity |
| Brahmi | Thyme leafed gratiola | Bacopa monniera Pennel Pennel | Enhances Memory, Anxiety |
| Kalmegh | Kalmegh | Andrographis paniculata Pennel | Indigestion, Acne, Diarrhea |
| Punarnava | Spreading Hogweed | Boerhaavia diffusa Linn Pennel | Anaemia, Liver Diseases, Wounds |
| Tulsi | Holy Basil | Ocimum sactum Linn Pennel | Indigestion, Heart Diseases, Respiratory Diseases |
| Vridhadaru | Elephant Creeper | Argyreia speciosa Sweet Pennel | Diabetes, Skin Diseases, Wounds |
| Agarkasth | Eagle Wood | Aquilaria agallocha Roxb Pennel | Bed-Wetting, Incompetency of Urinary Bladder |
| ee Kunwar | Aloes | Aloe vera Tourn ex. Linn Pennel | Ulcers, Burn Injuries, Jaundice, Acne |
| Palasha | Bastard Teak | Butea monosperma Kuntze Pennel | The complexion of Skin, Worm Infestations, Roundworm |
| Shirish | Siris Tree | Albizia lebbeck (Linn) Benth Pennel | Bronchial Asthma, |
Symbolic uses of plants
In art
Plants appear in art as decoration or symbolism. For example, the Virgin Mary was compared to a lily, where the white petals represent the purity of her body, while the yellow anthers signify her radiant soul. Several European portraits of her Annunciation also depict a vase of white lilies in her room to show these attributes.
Ancient architecture also showcases plants. For example, the Ancient Egyptian columns, are carved to resemble the Egyptian white lotus or the papyrus. Ancient Greek ones are decorated with acanthus leaves. Islamic art as well as architecture also frequently make use of plant motifs and patterns.
In literature and film

Both real and fictitious plants play a wide variety of roles in literature and film. A Plants’ roles may be evil, as with carnivorous plants or poisons ones, as well as mobility provided by three-foot-long appendages, from John Wyndham’s 1951 novel The Day of the Triffids. James Cameron’s 2009 film Avatar features a giant tree, Hometree, which serves as the sacred gathering place of the Na’vi tribe. In the movie, the interconnected tree, tribe and planet are threatened by mining and the film’s hero fights to save them all.
Trees are also common subjects in poetry. For example, Joyce Kilmer’s 1913 poem named “Trees”. Flowers are the subjects of many poems by renowned poets like William Blake and Rabindranath Tagore.
In mythology and religion

Plants figures appear in mythology as well as religion to symbolise growth, fertility and immortality. Some examples are,
- In Latvian mythology, a tree named Austras koks grows from the start of the Sun’s daily journey across the sky.
- Yggdrasil or the World Tree from the Norse mythology is the one on with Odin hung.
- The barnacle tree was believed to have barnacles that opened to reveal geese. This story began due to the observation of goose barnacles growing on driftwood.
- Greek mythology mentions the lotus tree that bears a fruit that causes drowsiness, and while moly, a magic herb mentioned in the Odyssey. The lotus is a religious symbol also shared between Jainism, Budisim and Hinduism. It represents the purity of the body, mind as well as speech. It is also often depicted floating above the murky waters of attachment and desire.
- The Bodhi Tree is the sacred fig tree under which Buddha is said to have attained enlightenment.
FAQs
1. What are the uses of leaves?
Uses of a leaf: for the plant
The leaves are the ones that produce food for the plant. It helps trap sunlight as well as aids in transpiration. Leaves also help in the exchange of oxygen and carbon-di-oxide.
Uses of a leaf: for humans
- Leaves are used as food. For example, cabbage, spinach and other leafy vegetables. A sizable quantity of our daily diet consists of some kind of leaf. In fact, a diet with more leafy material is considered to be healthy. Leafy foods are rich in minerals, vitamins, trace elements as well as fibre.
- A large number of Ayurvedic medicines come from leaves. For example, leaves of the neem tree, hibiscus, tulsi (basil), Aloe and papaya plant are used almost daily.
- Essential oils are extracted from leaves like mint, mentha etc for use in cosmetics, soaps or candles.
- Grasses, pearl millet, lucerne, maulshree, etc are great fodder for dairy animals.
- Leaves of khajur and coconut are used by the cottage industry to produce numerous decorative items like mats and handheld fans.
- Leaves of coconut as well as palm are used for making temporary housing in villages.
- Tobacco, chrysanthemum, neem etc are used for insecticide preparation from their leaves. Such insecticides are safer and thus are in great demand.
2. Which part of the plant do we use the most?
The part of the plant we use the most is the one that stores starch. When we consume corn or peas we are eating seeds, when we eat a carrot or beet we are eating the roots. Similarly, we eat the flowers of cauliflower as well as broccoli. Sometimes, we consume more than one part of the plant. For example, the root of the beet plant is what most people eat, however, its leaves can also be consumed.
3. What are edible parts of plants?
Not all parts of a particular plant are edible. But all edible parts are used a raw or cooked food. Generally, the leaves, roots, tubers, seeds, flowers, fruits and stems are edible. The most commonly edible part is the fruit, which is fleshy and succulent.
4. Do plants need humans to survive?
Yes, plants require animals or humans to survive. Although plants can produce their own food, they require humans as well as animals for pollination and continuation of the species.
5. Why are most plants green?
Chlorophyll is a pigment produced by the plant that gives it its green colour. They look green as the plants do not absorb the green wavelength of white light. Hence, the green wavelength falls on our eyes, making plants more ap green. Plants require chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
6. What is the importance of a cotton plant?
Cotton is one of the most essential fibres and cash crops in India. Due to its many uses, cotton plays a dominant dominant role in the industrial and agricultural economy of the country. A cotton plant provided cotton, the primary raw material in the cotton textile industry.
7. How do plants help the environment?
Plants provide oxygen
Through the process of photosynthesis, plants release oxygen back into the atmosphere, thus, giving humans and animals more air to breathe. Phytoplanktons are single-celled plants that produce the most oxygen in the atmosphere. Green terrestrial plants make up the rest.
Carbon sinks
Plants play a major role to help mitigate the effects of climate change. The biggest issue the world is facing is the abundance of carbon dioxide generated due to burning fossil fuels. Although this is common knowledge, we can not stop using fossil fuels as there is no other alternative to satisfy our energy needs. Till the time we find an alternative, we can lessen the amount of carbon dioxide in the air by planting more trees as well as plants. Terrestrial and oceanic plants are carbon sinks as they have the ability to store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Important carbon sinks around the world include boreal forests, grasslands, tropical rainforests, coral reefs, wetlands and coastal ecosystems.
Habitats are created by plant diversity
Plants provide habitats for wildlife and humans. For example, many species of birds rely on different shrubs and trees for shelter. Healthy habitats also shelter wildlife from predators. Unfortunately, habitat loss is considered a cause of species extinction. Forest ecosystems continually face deforestation in the form of cutting for agriculture and housing, forest fires as well as unsustainable logging.
Plants feed everyone
Plants are primary producers, that is, they are capable of producing their own food. Thus, they play an essential role in feeding all the wildlife and humans on the planet. Herbivores, rely on plants directly to meet their dietary needs, while carnivores feed on animals that consume plants. Omnivores, on the other hand, rely on both.
Water cycle regulation
About 10% of the moisture in the air is released by plants via transpiration. Plants take up water through their roots and release water vapour through small pores on the underside of their leaves. This process helps circulate water from the soil back into the atmosphere. Furthermore, plants help stabilize bodies of water like lakes, rivers as well as streams. Plant roots also improve soil stability, thus preventing landslides and keeping the ecosystem intact.
8. What are the benefits of growing plants at home?

Plants reduce stress
Research has shown that plants reduce stress. Seeing greenery around you has a calming effect by lowering blood pressure and therefore making you feel more relaxed and happier.
Plants in the home can prevent a blocked nose
Having plants around you can help reduce your chance of catching colds by up to 30%. Foliage increases the humidity in the space and removes airborne dust particles. Thus, you will be sneeze-free.
Plants have air-cleaning qualities around the home
Not only do plants collect dust particles, but they also help break down harmful substances in the atmosphere. They reduce carbon dioxide in the air and convert it into oxygen during the day. Healthy humidity, as well as high oxygen, improve the quality of air in your home. Epipremnum and Spathiphyllum are especially good air-purifying plants.
Plants combat cigarette smoke
Plants filter toxins that are in cigarette smoke. Therefore, if you have a smoker in your house then, plants like Spathiphyllum also known as the peace lily, are a good choice.
Plants improve the acoustics in the house
The leaves of plants can absorb background noise, thus, improving the acoustics in your home. Thus, it is a good idea to add some house plants to create a quieter living environment and workspace.
Plants help improve your mood
Several studies show that plants help combat depression. Plants ensure a better state of mind by providing positive energy as well as an increased sense of happiness.
Plants reduce the risk of headaches
The air-purifying property of plants can also reduce headaches. Research shows that plants can remove benzene, formaldehyde and trichloroethylene from the air. These are common causes of headaches and are used in the production of carpets as well as leather sofas.
9. Which plant is used to make linen?
Linen, one of the oldest human fabrics, is obtained by weaving fibres of the flax plant. The fibres, which are in the stalk are picked by hand and processed. Then, they are spun into yarns and woven into linen textiles. Linen is a popular material of choice for sheets, table cloths, dresses, suits as well as blazers.
Share with your friends