It is a relatively tough task to make the children understand the basic concepts of grammar. Grammar is a little bit complex though very interesting concept. Parts of speech has a wide definition. For instance, adverbs, nouns, adjectives, prepositions etc.
The parts of speech are entrusted with the task to explain that how a word is used in a sentence. Since, there are eight main parts of speech in total and each of these parts of speech has its own different-different importance. Moreover, they all are further divided into subclasses.

What are the parts of speech?
So, let’s begin with the explanation of what are parts of speech.

A part-of-speech is a classification of words that have identical grammatical properties.
English plays a very crucial role nowadays in every part of the world. We can not overemphasize the importance and usefulness of the English language these days.
English has a role to play at various places ranging from school, office, home etc. Parts-of-speech refers to the words in a sentence and the role it plays. Different roles are played by different words in a sentence.
We all know the basics of parts of speech. We even use these in daily life without knowing the exact meaning.
Nine parts are used to convey our messages.
The 9 parts of speech include nouns, pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, Articles, and Interjection.

What are the different parts of Speech?
Nouns
The names of any person, place, thing, animal, or idea are considered nouns. A noun plays the role of a subject( whether direct or indirect) or adjective. Examples of Nouns are the Taj Mahal, Geeta, Lucknow, Pin, Ball, Albert Einstein, and Elephant.
There are different types of Nouns. The different types of nouns are Common Noun, Proper Noun, Abstract Noun, Collective Noun including Concrete Noun, Count and mass Noun, etc.
Common Nouns are those nouns that generally apply to the names of people or things. For instance, boy, Country, City, Book, Bat, Tea, etc.
Proper Nouns identify the particular name of a person, place, animal, or thing. Like Alexander, Lucknow, Delhi, London, America, etc. To be sure of Proper Nouns, it starts with Capital letters in English while writing.
Concrete Nouns are nouns which are referred to people and things that occur physically and can be seen, touched or smelled including Tea, Coffee, Tree, House, Biscuit, etc.
Abstract nouns refer to ideas and qualities which cannot be smelled, touched, or seen. For example happiness, anger, sadness, friendship, etc.
Pronoun

Pronouns are the words that are used in place of nouns. For instance: He, she, they, themselves, each other, it, etc. Pronouns are used in our daily life. Also, Pronouns help us to make our conversation easy and more convenient.
The most common pronouns are the personal pronouns, which refer to the person or people speaking or writing (first person), the person or people being spoken to (second person), or other people or things (third person). Like nouns, personal pronouns can function as either the subject of a verb or the object of a verb or preposition: “She likes him, but he loves her.” Most of the personal pronouns have different subject and object forms
For instance:
- Riya loves watching cricket. Riya also knows well the rules of cricket and Riya can play cricket too.
On the other hand, instead of using ‘Riya’ again and again. Using ‘She’ is the correct option.
- Riya loves watching cricket. She also knows well the rules of cricket. She can play cricket too.
In Addition, There are various categories of pronouns like Personal pronouns, Antecedents, and Relative Pronouns, Demonstrative Pronouns, Indefinite Pronoun, Reflexive Pronoun, Intensive Pronoun, Possessive Pronoun, Interrogative pronoun, Reciprocal Pronoun, Distributive Pronoun, etc.
Types of Pronouns
Possessive pronouns- mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs
- That scarf on the table is mine.
Personal pronouns- I, you, she, he, it, we, they, me, us, them, etc.
- I am afraid of darkness.
Relative pronouns- who, whom, which, what, that, etc.
- I need to find a person who can host the Japanese.
Reflexive pronouns- myself, yourself, itself, herself, himself, ourselves, themselves, etc.
- Jeremy looked at herself in the glass.
Intensive pronouns- lf, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, themselves, etc.
- I made the sweet dish myself.
Indefinite pronouns- some, somebody, anyone, anywhere, nothing, everybody, etc.
- Someone stole my purse.
Demonstrative pronouns- this, that, these, those, etc.
- This is my favorite dish.
Interrogative pronoun- who, whom, what, which, whose, etc.
- Who did this?
Reciprocal pronouns – each other, one another, etc.
- We like each other.
Adjective

Adjectives are words that describe the quality of nouns or pronouns. The adjectives are placed before the noun or pronoun. For instance, small, blue, big, round, many, sharp, etc. Let us understand Adjective more clearly with the help of a sentence.
Some adjectives describe qualities that can exist in different amounts or degrees. To do this, the adjective will either change in form (usually by adding -er or -est) or will be used with words like more, most, very, slightly, etc.: “the older girls,” “the longest day of the year,” “a very strong feeling,” “more expensive than that one.” Other adjectives describe qualities that do not vary—”nuclear energy,” “a medical doctor”—and do not change form.
- Jennifer is a sweet girl. (Significantly, note that adjectives don’t need to be placed before the noun or pronoun)
Here, in this sentence, the word ‘sweet’ is an example of an Adjective. It describes the quality of our noun ‘Jennifer’.
There are various types of Adjectives like
- Possessive Adjective (For example – my, his, your, our, etc.)
- Demonstrative Adjectives like these, this, those, etc.
- Coordinate Adjective (These adjectives are separated by ‘commas’ or ‘and’. For Example – ‘Bright, sunny day’.)
- Numbers Adjective like six, ten, etc.)
- Interrogative Adjective like which, what, whose, etc.)
- Indefinite Adjective as many, several, few, etc.)
- Attributive Adjective (For instance – perfect, poor, young, pink, French, gold, etc.)
Verb
The words that describe the actions in a sentence are called Verbs. The verbs generally display what the subject is doing in the sentence. Examples of verbs include playing, singing, running, jumping, love, hate, thinking, etc. Let us understand verb verbs clearly by taking some sentences as examples.
- Ritu is playing with her game.
Here ‘Ritu’ is the subject and the word ‘playing’ describes the actions of ‘Ritu’. Hence ‘Playing’ is a Verb.
- The girl is dancing in the rain.
Here, ‘Dancing’ is the verb in this sentence.
Types of Verbs
There are different types of verbs which include Dynamic Verbs, Static Verbs, Auxiliary Verbs, Modal Auxiliary Verbs, Phrasal Verbs, Linking Verbs regular Verbs, and Irregular Verbs.
Examples of Phrasal Verbs
- ask for
- put up with
- talk down to
- lock up
- cut across
Irregular Verbs
- be becomes am, is, are, was, were, be, being, and been
- eat becomes ate, eaten
- fly becomes flew, flown
- catch becomes caught, caught
Regular Verbs
- jump becomes jumped
- slip becomes slipped
- try becomes tried
- sleep becomes slept
- lend becomes lent
Linking Verbs
- be
- become
- seem
- appear
- grow
Helping Verbs
- be
- have
- do
- can
- will
Modal Verbs
- can
- may
- might
- must
- would
Stative Verbs
- love
- want
- own
- have
- resemble
Action Verbs
- run
- swim
- help
- ignore
Adverbs

One of the parts of speech. These words generally modify an adjective, verb, clause, determiner, preposition, or maybe another adverb. In simpler words, an adverb is a word that describes a verb, adjective, sentence, or another adverb’.
Let us try to comprehend Adverb adverbs example.
- The tree is very tall.
In the above statement, the word ‘tall’ describes the verb ‘tall’. Hence ‘tall’ is an adverb.
Other examples of Adverbs include-
- Rani loves her red cap.
- The show finished too quickly.
- Riya sings loudly in the lobby.
- The girl is quite gorgeous.
Just like other parts of speech i.e, Nouns, pronouns, verbs, there are different types of Adverbs. The different types of Adverbs are mentioned below-
- Conjunctive adverbs
- Adverbs of frequency
- Time Related Adverbs
- Manner Related Adverbs
- Adverbs of degree
- Adverbs of place
Above all, These are the six most common types of adverbs.
Conjunction
A conjunction is a word that is used to join two words in a sentence. It generally acts as a junction between two words. Also the conjunction can join two nouns, two pronouns, two adjectives, two phrases, or two clauses.
Significantly, note that seven Conjunctions can be easily remembered by using the acronym FANBOYS:
For And Nor But Or Yet So.
There are various conjunctions other than these seven like rather, not, both, etc. The usage of these some conjunctions are reflected in the given sentences:
- Riya likes playing and studying both.
- You can either participate in dance or singing.
- Ryan neither likes badminton nor cricket.
There are basically three types of conjunctions which are Coordinating conjunction, Correlative conjunction, and Subordinating conjunction.
Subordinating Conjunction (For instance – after, although, unless, because, in order, since, etc).
Examples of Coordinating conjunction are for, and, neither, but, or, yet, so, etc.
Correlative Conjunction are only…but also, either….or, neither….nor, through….yet, etc.
Preposition

Understanding prepositions can be a little bit confusing for us but Prepositions are words that inform us when and where something is in association with something else. Also, prepositions can tell us where one noun is in relation with the other. Let us take an example to understand it more clearly.
- The hat is on the chair beside you.
Here the words ‘on’ and ‘beside’ tells the relationship between two nouns ‘hat and ‘chair’. Prepositions generally tell us where and when something happened.
Another example of the preposition is mentioned low.
- We went for a drive despite the storm.
Preposition generally reflects direction, period, location, space, and some other types of abstract relationships.
Here are some examples provided for your better understanding.
- Move your head to the left and you can see the building.
- The cat hid under the bed.
- We have been resting since morning.
Articles
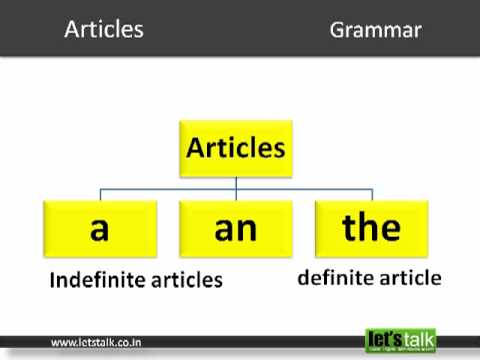
Articles are noun that is used to define or modify the noun as specific or unspecific. These words generally define the noun. Articles are usually used before the noun. Articles can also be considered as a type of adjective as adjectives also are used to tell something about the Noun. Sometimes we consider the articles as a type of adjective too.
In the English language, there are two types of articles, Definite articles, and Indefinite articles.
Certainly, definite articles are used about a particular thing or person. Definite articles demonstrate that the noun is specific. ‘The’ is a definite article that is used in the English language. Examples of usage of the definite article are listed below.
- The English dictionary is on the table.
- The boy sat on the bed.
- I liked the necklace.
Indefinite articles are used where the identity of the noun is not clear. The word ‘indefinite’ refers to something which is not clear. The indefinite articles in the English language are considered ‘an’ and ‘a’. The examples of indefinite articles are listed below.
- I want a pet cat.
- Siya wants to have an apple.
- I would love to have a ride.
Interjection

Words that rather express our feelings in a sentence and are grammar independent considered Interjections. For example: Alas, oh, wow, shit, ugh, etc.
Given below are few examples of how to make use of interjections in different different sentences are given below.
- Oh, what a good-looking horse!
- Uh-oh, this seems so creepy.
- Well, it’s the moment to say good evening.
- Certainly, um, it’s not my puppy.
- Shoot. I guessed I’d cured that.
- I can’t imagine I misplaced the books! Ugh!
- Ugh! This is so frustrating!
- Hurray! I passed the exam.
- Yay, we’re going to Manali.
There are some rules when we use Interjections. While using interjections in a sentence, either we have to put them in parenthesis or set it off with commas as shown in the above sentences.
We can use interjections in different ways such as informal writing, casual speaking, or in speech too. However, the issue with interjections is that we cannot use interjections in formal writings.
Sentences with all parts of speech
- In the midst of the ring, the two tired boxers feel gloves and tentatively exchange punches until — oh! — down goes the champ!
In the midst- Preposition, article, noun, Of the ring- Preposition, article, noun, The two tired boxers- article, adjective, adjective, noun.
Feel gloves and- verb, noun, conjunction, Tentatively exchange punches- adverb, verb, noun, Until- subordinate conjunction, Oh!- Interjection and Down goes the champ- adverb, verb, article, noun
- Ah! it was a fascinating movie and people hurried fast to book ticket.
Ah!- Interjection, It- pronoun, was- verb, fascinating- adjective, Movie- noun, And- conjunction, People- Noun, Hurried- verb, fast- adverb, to- preposition, book- verb, tickets- noun
- Egads, the horrible professor assigns us homework daily and wants it on his desk by eight the next day!
Egads – Interjection, horrible – adjective, professor – noun, assigns – verb, it – pronoun, daily – adverb, and – conjunction and preposition – on
- Ah! My partner and I desire we could travel yearly to Europe and take in all the wonderful locations.
Ah – Interjection, wonderful – adjective, partner – noun, Desire – verb, we – pronoun, yearly – adverb, and – conjunction and to – preposition
- Rocky ran quickly to the brown dog, and said to him, “hey!”
Noun- Rocky, Verb- Ran, Proposition- to, Adverb- quickly, Interjection- Hey!, Conjunction- and, Adjective- Brown and Pronoun- him
Important Points
To be noted, just like Y is considered both vowel and consonant depending upon time, there are words that are sometimes one part of speech and other times another. Some examples are listed below:
- Work
- I went to the office for work (noun).
- I work in the department store (verb).
- Well
- She did very well in the examination (adverb).
- The area is well-developed in his colony (adjective).
- I dropped my gift in the well(noun).
- But
- I made the breakfast and lunch, but Steve cooked dinner (conjunction).
- I revised everything but forgot to learn the lesson you asked for (preposition).
The usefulness of parts of speech.
Now after learning the 9 parts of speech and their examples, we should also know, what is the benefit of knowing them? Because it is very important to understand the usefullness of it. Well there a lot of benefits of learning the parts of speech. Here are some points which tell us the benefits of learning parts of speech.
- Understand which words to capitalize.
2. We can frame sentences without any mistakes and more effectively.
3. Learn which words need an apostrophe to form the possessive.
4. Knowing when to put a comma to attach two sentences correctly is very important.
5. Utilize the right tags to find information in a search.
6. We can disagree positively with people’s out-of-date rules.
7. We can learn English more effectively by learning these parts of speech.
We will easily know how and where to use the words in our sentences. It also helps us to master our writing techniques.
Understanding of essence of words, sentence pattern, and parts of speech have a great part to play in comprehension and writing.
Become a professional Content Writer from the comfort of your home.
Sign up for Podium Pro and get a chance to create awesome content for top global brands!
Parting words
Grammar has a very crucial role to play in English itself. Parts of speech are very useful once they are understood in depth. Once remembered with clarified concepts, then it is very easy to do their careful application in any sentence. Their identification and application becomes very easy.
We hope that you liked reading the blog. Also, we sincerely hope that you got whatever you were looking for. We tried to put all the relevant information that was necessary to be placed under this one blog so as to make it fully enriched with information. We wish to see you again. Till then, have a happy reading !
Conclusion
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. The parts of speech are important because they show us how the words relate to each other. For example, let’s take the words “hit,” “Kevin” and “Brian.” Now, they are just words, they don’t really tell us something. But if we use it with any of the parts of speech. For instance
- Sssssshh! Keep Quiet Kevin. (Interjection)
- Brian is a hardworking person.(Adjective)
Visit Podium School’s Official website for more information. Stay Tuned…..
Frequently Asked Questions
We have listed below, few frequently asked questions about parts of speech.
1- What are determiners? What are few of its examples?
A determiner is a word which is placed in front of a noun to specify the quantity of the noun.
2-Why is learning parts of speech important?
The parts of speech are very important. The reason of their importance is that they show us how the words relate to each other in grammar.
3-Will learning parts of speech help me in improving my writing skills?
Parts of speech in grammar is actually the building block of sentences. Also, it is impossible to write grammatically correct sentences if you do not know at least some of the Part of Speech. Learning part of speech is surely going to help you in improving your writing skills.
4-What are simple adverbs? What are few of its examples?
Simple Adverbs contain only one word and they are the most used Adverbs. For example, Please wait.
5- What are the twelve different types of parts of speech?
Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, or determiner are the twelve different types of parts of speech.
6-How do you identify part of speech in a sentence?
To identify different parts of speech, analyze the function that the word plays in a sentence. If the word names a person, place, thing, or idea, it is a noun. Label a word as a pronoun if it takes the place of a noun. If you see a word that expresses an action, that is a verb, and words that modify a verb are adverbs.
Share with your friends