A noun is the portion of the speech that is used to designate a person, place, thing, quality, or activity. In addition, it can serve as a verb’s subject or object, a preposition’s object, or an appositive. This time, we bring you a perfect guide to the Types of Nouns that are frequently used to formulate a variety of sentences.
10 Types of Nouns
Here are 10 types of nouns:
- Common Nouns: These are general, everyday nouns that refer to people, places, or things. Examples include “dog,” “city,” and “book.”
- Proper Nouns: These are specific names of people, places, or things and are capitalized. Examples include “John,” “Paris,” and “The Great Gatsby.”
- Concrete Nouns: These are nouns that refer to tangible, physical objects that you can touch, see, or experience with your senses. Examples include “table,” “mountain,” and “rain.”
- Abstract Nouns: These nouns refer to ideas, concepts, or qualities that cannot be perceived by the senses. Examples include “love,” “happiness,” and “justice.”
- Countable Nouns: These are nouns that can be counted as individual units. Examples include “apple,” “car,” and “child.”
- Uncountable Nouns: These are nouns that cannot be counted as separate units because they represent a mass or a substance. Examples include “water,” “sand,” and “knowledge.”
- Collective Nouns: These nouns refer to a group or collection of people, animals, or things. Examples include “team,” “family,” and “herd.”
- Compound Nouns: These are nouns formed by combining two or more words. Examples include “toothbrush,” “bookshelf,” and “firefighter.”
- Possessive Nouns: These nouns show ownership or possession. They are often formed by adding an apostrophe and “s” (‘s) to the end of a noun. Examples include “dog’s bone,” “teacher’s desk,” and “children’s toys.”
- Verbal Nouns (Gerunds): These are nouns formed from verbs and end in “-ing.” They represent an action or activity. Examples include “swimming,” “reading,” and “writing.”
Understanding the different types of nouns can help you use language more precisely and effectively in your writing and communication.
Common Nouns
A noun that can be used with a limiting modifier to name a group of people or things, or any individual within that group, (like a, the, some, or every) “child”, ”city”, or “day”, are examples of common nouns. Let’s look at another example:
Q: “After entering the living room, what do you see?”
A: ”A lamp, a chair, a couch, a television, a window, a painting, a pillow, and a candle.”
As one can see, all these names are common nouns that are preceded by a limiting modifier, which is ’a’ in this case.

Proper Nouns
The name of a specific person, place, organisation, or thing is referred to as a proper noun. The initials of proper nouns are always written in capital letters. The noun, ’city’, isn’t a proper noun because it’s general and can refer to a variety of locations. However, that’s not the case when we mention ‘New York City’, ‘Paris’, ‘London’, ‘Beijing’ etc. These nouns are all proper nouns since they refer to distinct locations on Earth that can only be found in one place.
Singular Nouns
In English grammar, singular nouns are those that refer to only one thing, place, person, or instance. The word, ‘girl’, for example, is a singular noun, but the term, ‘girls’, cannot be called one because it refers to more than one person.
Plural Nouns
A plural noun is a type of noun which indicates that there is more than one object present. To make a plural noun, simply add –s or –es at the end of a singular noun.
Concrete Nouns
A concrete noun signifies something that can be seen, smelled, touched, felt, and tasted. In other words, these nouns refer to things that one can perceive with at least one of their senses. For instance, music, noise, rainbow and phone are concrete nouns.
Abstract Nouns
An abstract noun is a word that describes a quality or a concept. Nouns that name abstract notions, or concepts that cannot be experienced with the senses, come under the category of abstract nouns.

Collective Nouns
Collective nouns are used in everyday discourse, even if one doesn’t realise it. Individual entities made up of more than one person, animal, place, item, or idea are referred to as collective nouns. Even though a team cannot exist without individual members, we refer to it as a single entity. For example, a bale of cotton, a basket of fruit, a bundle of sticks etc, are some collective nouns.
Compound Nouns
Compound nouns are words made up of two or more words that refer to people, animals, places, things, or ideas. The majority of compound nouns are made up of nouns that have adjectives or other nouns preceding them. Therefore, in many compound nouns, the second word, which usually identifies the item, is described or modified by the first word. This gives us information about the type of item as well as its function. For example, fire-fly, greenhouse, bus stop, blackboard and software are some collective nouns.
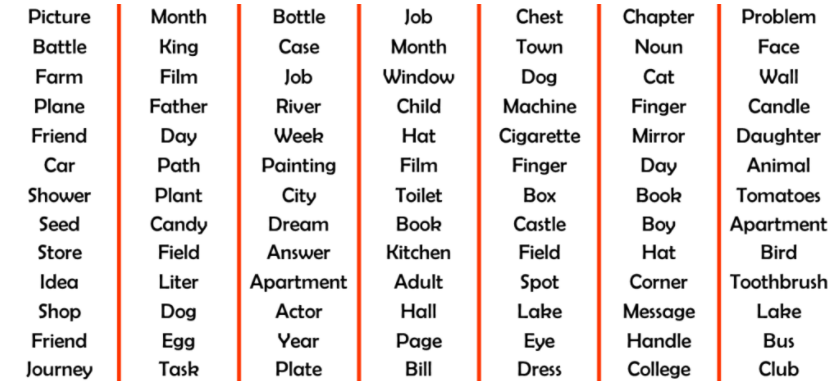
Countable Nouns
Countable nouns are things that can be counted. Cat/cats, woman/women, country/countries are examples of singular and plural forms of countable nouns respectively. In fact, singular nouns are generally preceded by either ‘a’, or ‘an’. The table given below lists some commonly used countable nouns:
Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable nouns are those that do not usually relate to objects that can be counted and therefore, do not have a plural form (or mass nouns). ‘Rain’, ‘bread’, ‘dirt’, ‘wine’, and ‘wood’ are a few examples of uncountable nouns. Many abstract words, such as ‘happiness’, ‘truth’, ’darkness’, and ‘humour’, are often uncountable as well. However, depending on the meaning or context of the word, some uncountable nouns are used in the plural, to begin with. Powders, police and groceries are plural unaccountable nouns.
What is the Special Rule of Proper Nouns?
Proper nouns have a specific rule which states that they must always be capitalised, regardless of their position in a phrase. ‘Cassandra’ is a proper noun that refers to a specific person, and is capitalised in the following example, even though it is not the word that initiates the sentence: “Tomorrow is Cassandra’s birthday.” Correct capitalization is one of the most prevalent grammar blunders. Therefore, knowing how to recognise proper nouns is very crucial.
Guide to Regular Plural Noun
Plural nouns are formed by appending the letter “s” to the end of the singular nouns. For example, we can take the singular noun ‘apple’ and add an “s” to form the plural noun ‘apples’. We can often notice that the plural noun is the ’plural form of X singular noun’. Another example of this concept is the word, ’bugs’, which is the plural form of the singular noun, ‘bug’. On the other hand, we append the suffix ‘–es’ to singular nouns that already end in ‘s’. For instance, to produce the plural noun, ‘buses’, we add ‘–es’ to the end of the single form of the word, ‘bus’. A similar pattern may be seen in terms like ‘guesses’, ‘dresses’, ‘biases’, and ‘losses’. Regular plural nouns are plural nouns that follow these simple principles.
However, some words are a little difficult, as they don’t always follow the standards, which results in the word having a change of spelling in its plural form. For example, the plural form of the word, ’marsh’, is ‘marshes’, while the plural form of the word, ’baby’, is ‘babies’.
Guide to How Nouns are Formed
As mentioned earlier, people, places, and things are all referred to by nouns. Interestingly, however, suffixes, defined as a letter or group of characters appended to the end of a word, can be used to create new nouns. For example, we can form the noun, ’action’, by adding a suffix, ’ion’, to the verb, ’act’.
Given below is a video that talks about some common errors to look out for while using nouns.
Conclusion
Nouns are one of the most commonly occurring elements in the English language. In fact, as we have seen throughout the article, there are different types of nouns that can be employed in a sentence in a variety of ways. Therefore, in order to construct flawless sentences, it is imperative to have a proper understanding of nouns and their applications in English grammar.
Share with your friends