Air pollution refers to the presence or release of harmful pollutants in the air. Pollutants are substances that are detrimental to human health and the planet as a whole. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), air pollution causes the death of almost seven million people worldwide every year. Hence, it is important to identify the causes and reduce pollution as soon as possible, in and halt the imminent danger to human life and the planet as a whole.
Did you know this about Air Pollution?
1. Over nine out of 10 people in the world live in an area where air pollution exceeds the safe limit.
2. Air pollution is the fourth-largest threat to human life. It is the primary cause of respiratory infections, stroke, cardiovascular diseases and lung cancer.
3. Air pollution-related deaths accounted for 11.6% of the total deaths in 2012, according to WHO data. This number is more than the people who died of HIV/AIDS, road injuries and tuberculosis combined.
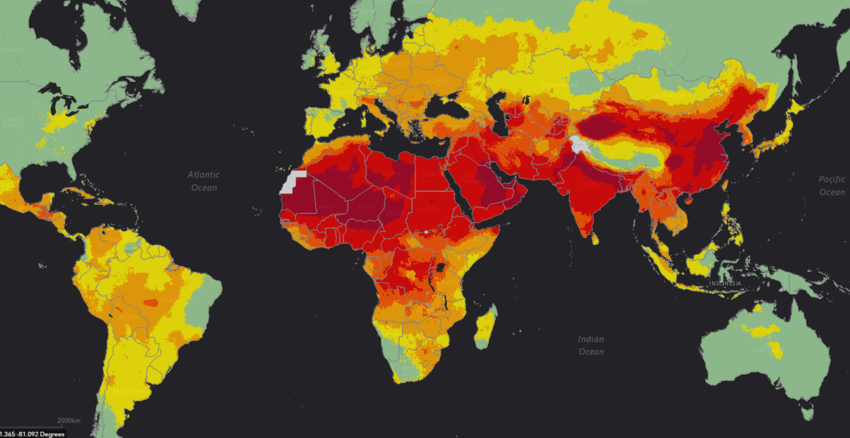
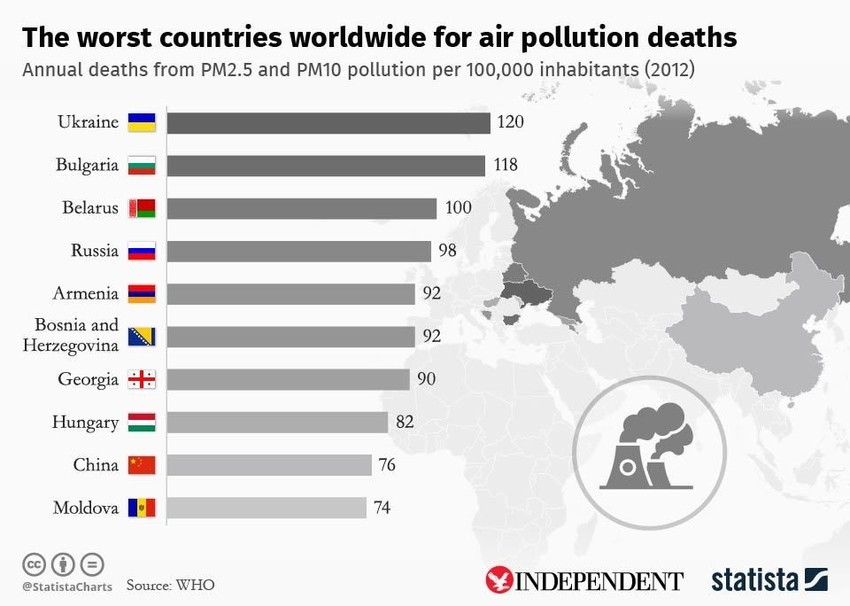
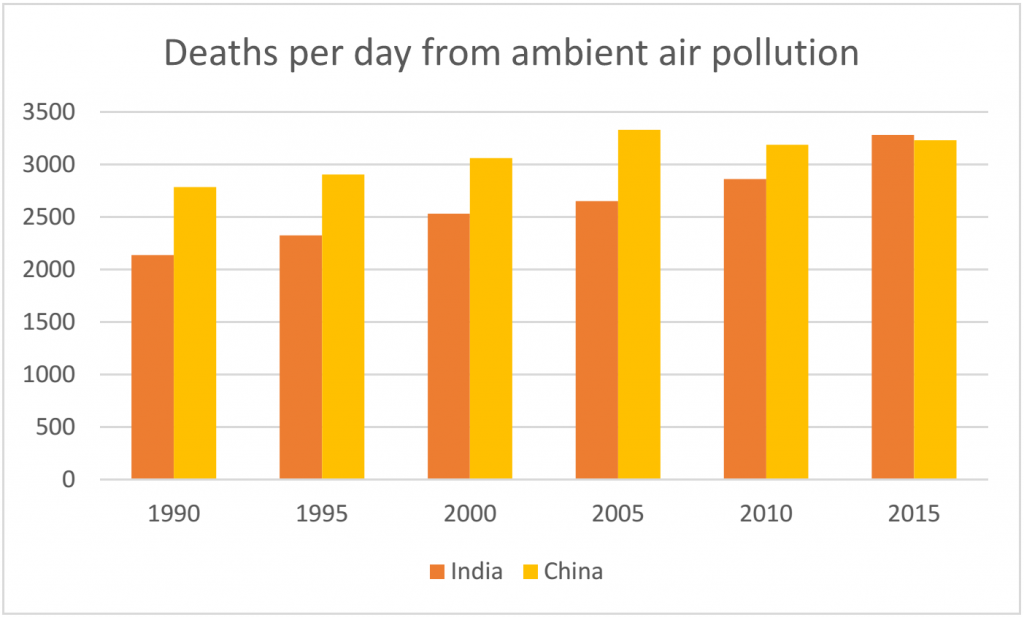
4. 92% of the deaths linked to polluted air occurred in middle or low-income countries. Hence, parts of Africa, India, Eastern Europe, the Middle East and China are dangerous spots. The highest deaths were recorded in Eastern Europe. The chart below details this information.
5. Air pollution causes more deaths in India than in China. An average of 3,283 premature deaths were recorded in India per day in 2015, while the number of premature deaths per day in China was 3,233.
6. Household air pollution contributed to 3.8 million deaths in 2016. This makes it one of the largest risk factors to human health.
7. Global carbon dioxide emissions totalled 31.5 billion metric tons in 2020. This is roughly six per cent lower compared to the previous year. Furthermore, this is the biggest annual reduction since World War 2.
8. Delhi was named the most polluted capital city in the world in 2020. Data shows the presence of 84.1 micrograms of PM2.5 per cubic meter of air (μg/m³). This concentration was almost 10 times higher than the World Health Organization target of 10 μg/m³.
9. The second most polluted capital was Dhaka in Bangladesh.
10. Many cities experienced reductions in PM2.5 pollution in 2020 due to restrictions on economic activity during the outbreak of COVID-19.
What are the sources of air pollution?
Here, we will discuss the most common air pollutants and their sources. The common air pollutants are:
Particulate matter or PM
Particulate matter refers to extremely small solid and liquid particles that are suspended in the air. PM can be made of different components like sulfates, metals, dust particles, soil, nitrates, organic and allergens. There are two sizes of particles present in the air. Firstly, PM10, which are particles with a diameter of less than or equal to 10 micrometres. These particles are small enough to pass through the nose and throat and enter the lungs. Once there, they can adversely affect the heart as well as lungs and cause serious health effects. The second type of particle is known as PM2.5. These particles are less than 2.5 micrometres and are so tiny that they can go deep into the lungs and the bloodstream.
Ozone or O3
Ozone is three oxygen atoms bonded together. Two oxygen atoms bonded together create the basic oxygen molecule (O2). The third atom makes ozone an unstable and highly reactive gas. Ozone is found both in the Eath’s upper atmosphere as well as at surface level. In the upper atmosphere, ozone protects people by filtering out damaging ultraviolet radiation from the sun. However, at ground level, ozone is damaging to human health.
Ground-level ozone results from the interaction between the sun rays and emissions from motor vehicles or industries. It is the primary component of smog and it causes several health problems like sore throat, coughing and reduced lung function.
Nitrogen Dioxide or N02
Nitrogen dioxide is a highly reactive gas emitted by motor vehicles, gas heaters, industries and gas stovetops. High concentrations of the toxic gas are found on busy roads and indoors where gas heaters are in use.
Other indoor sources can be from cooking with gas or cigarette smoke. Outdoors, nitrogen dioxide contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone as well as PM pollution. Nitrogen dioxide causes several adverse respiratory problems.
Carbon monoxide or CO
Carbon monoxide is a colourless and odourless gas, created when the carbon in fossil fuels or biological matter do not burn completely. Motor vehicles and industries are the primary sources of carbon monoxide. Indoors, carbon monoxide is formed by gas heaters or wood-burning heaters.
Carbon monoxide levels are highest during cold weather as low temperatures do not allow complete combustion of the carbon fuel. Carbon monoxide is poisonous as it reduces the amount of oxygen reaching the different organs. Some symptoms include dizziness, impaired vision and confusion.
Sulphur dioxide or SO2
Sulphur dioxide is a highly reactive gas that has a pungent and irritating smell. It is formed by the combustion of fossil fuels at power plants and other industrial facilities. However, some natural processes also release sulphur gases. For example, decomposition and combustion of organic matter, volcanic eruptions and spray from the sea.
Sulphur Dioxide contributes to the formation of PM pollution. It irritates the lining of the nose, throat and lungs and may cause several respiratory problems.
Sources of the pollutants
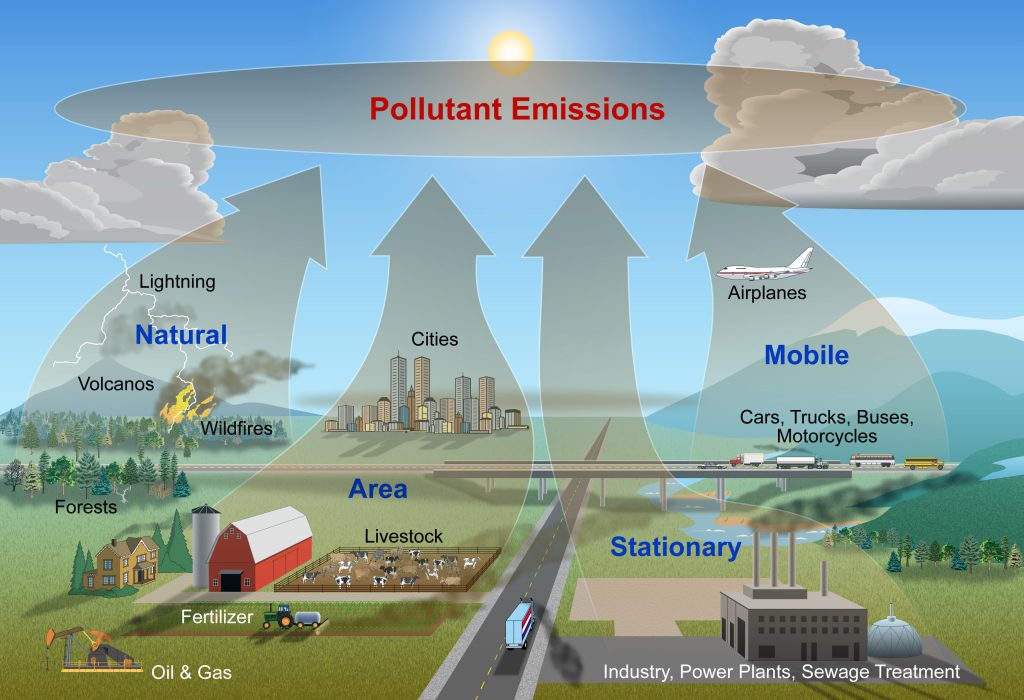
Natural sources
There are several natural air pollution causes. These include:
1. Volcanic activities emit several toxic gases like sulfur and chlorine as well as particulate matter.
2. Wind currents mobilize pollutants from the ground and carry them over large areas.
3. Wildfires contribute to air pollution by adding carbon monoxide and particulate matter to the atmosphere. These fires are generally restricted to small areas.
4. Microbial decay majorly contributes to environmental contaminants. This activity results in the release of toxic gases.
5. Radioactive decay emits radon gas which accumulates in enclosed spaces like basements.
Man-Made Sources
Man-made sources include:
1. High temperatures due to global warming contribute to an increase in the number of volatile contaminants in the air from polluted water and soil.
2. Mining and smelting emit metal particles in the air.
3. Foundry activities or processing of raw metals release metals that are absorbed on particulate matter.
4. Industries release both inorganic and organic contaminants through leaks and accidental spills of stored chemicals.
5. Motor vehicles release a series of air pollutants like gasses (nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide) as well as particulate matter through the tailpipe.
6. Construction and demolition activities pollute the air with different chemicals and compounds. When old buildings are demolished, they release banned chemicals like asbestos, PCBs and PBDEs.
7. Coal power plants emit gases as well as particulate matter with metals while burning coal. Additionally, they release contaminating organic compounds.
8. Heating of buildings using gas heaters contributes to carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide in the air.
9. Waste incineration releases various toxic gases and particulate matter into the atmosphere. The same goes for landfill disposal, which usually generates methane.
10. The pesticides, herbicides and insecticides used in agriculture pollute the air with ammonia gas and other toxic organic compounds.
11. Military activities introduce toxic gases and particulate matter into the atmosphere.
12. Smoking emits a series of toxic organic and inorganic chemicals, some of which are carcinogenic.
13. Products like sprays, paint, varnish, etc, release volatile compounds into the air.
14. Dry cleaned clothes emit small amounts of chlorinated solvents or petroleum solvents, which can create a health risk if the clothes are stored in enclosed indoor spaces.
What are the effects of air pollution?
Air pollution affects the following,
Effects on human health
According to the World Health Organization, ground-level ozone gas causes muscles in the lungs to contract, thus, making it difficult to breathe. Additional symptoms include sore throat, lung inflammation, coughing, and permanent lung damage. The image below describes the effect of ozone on the lungs.

Exposure to air pollution can be of two types:
- Short term exposure-This resolves fairly quickly.
- Long term exposure- This, on the other hand, is linked to serious illnesses.
| Short term exposure to air pollution can cause | Long term exposure to air pollution can cause |
| Coughing | Respiratory diseases (Asthma, Emphysema) |
| Wheezing/Difficulty breathing | Cardiovascular damage |
| Irritation to eyes, nose, and throat | Harm to liver, spleen, and blood |
| Headache | Nervous system damage |
| Dizziness | Cancer |
| Fatigue | Birth defects |
| Death |
At-risk groups for air pollution-related health problems include:
- The elderly, children and people with ongoing illnesses are more susceptible to air pollution health problems than other groups.
- Urban populations are also at greater risk due to elevated concentrations of pollution within cities.
Effects on plants and animals

Wildlife can also experience many of the negative health effects of air pollution like humans do. This includes damage to the respiratory system, neurological problems and skin irritations.
Furthermore, plants and crops grow less when exposed to long long term air pollution. Ozone pollution damages structures called stomata, which are tiny pores on leaves that allow the plant to “breathe.” While some plants can protect themselves by temporarily closing their stomata, others are particularly sensitive to damage. From 1980 to 2011, the United States lost nine billion dollars worth of soybeans and corn to ozone pollution, coupled with acid rain, lead toxicity, and exposure to nitrogen oxides. Thus, air pollution greatly impacts forests, agriculture, and grasslands.
The other ways air pollution hamper living things include, damage to habitat, water and food sources.
Causes acid rain

Burning fossil fuels release sulfur and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. Acid rain forms when this sulfur and nitrogen dioxide mix with water droplets in the atmosphere and result in the formation of sulfuric acid and nitric acid. Winds can carry these acids over large distances until they fall to the surface as acid rain.
Acid rain damages plants, buildings and increases the acidity of soil and water. It is linked to over 500 deaths and damage to approximately five billion dollars worth of property each year. It dissolves mortar between bricks, thus causing stone foundations to become unstable. This usually happens in ancient or old buildings.
Reduces sunlight on the surface
High levels of particulate pollution, reduces the amount of sunlight that reaches the surface of the Earth. Furthermore, it can even change the visibility and appearance of the sky. If less sunlight is available for photosynthesis, crops become less productive and forests grow slower.
Makes a hole in the ozone layer

As we already know, the protective ozone layer is depleting in certain areas, thus exposing people to harmful ultraviolet rays. The hole is caused by air pollutants. Chemicals used as refrigerants, like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), contain chlorine atoms. Chlorine atoms react with the ozone molecule in the atmosphere and destroy it. A single chlorine atom can bond with thousands of ozone molecules, thus, creating a hole in the ozone layer.
High amounts of UVB that reaches the surface increases the risk of skin cancer in humans, restrict growth and development in plants, fish and amphibians. Furthermore, the number of phytoplankton in marine ecosystems reduces. UVB also causes synthetic and natural materials to break down at an accelerated rate.
Adding Too Much Nitrogen to the Land
Gaseous ammonia from agriculture practices and nitrogen dioxide released from motor vehicles increase the amount of nitrogen in soils. Although plants need nitrogen to grow, too much nitrogen can limit or increase the growth of others, thus, disrupting the balance of species in the ecosystem.
Greenhouse gas pollution and global warming
Greenhouse gas pollution causes climate change faster than plants and animals can adapt to it. Therefore, many species are going extinct. Marine ecosystems like coral reefs are vulnerable to ocean acidification caused when carbon dioxide in the atmosphere dissolves in seawater. Acidic water hampers the growth of shells and skeletons in marine animals.
Finally, global warming, caused by heat trapped due to high amounts of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, has led to the melting of ice caps, warming of oceans and extreme climate changes. These changes threaten ecosystems across the earth.
Indoor Air Pollution
Indoor, air pollution is caused by the following,
- Heating homes by burning carbon-containing substances like kerosene, coal and wood. This can contaminate the air the house, thus, making it difficult to breathe.
- Furthermore, burning releases substances like ash and smoke that stick to walls, clothing and food, leading to long term exposure to pollutants.
- Naturally-occurring radon gas can also build up in homes. It is released by the surface of the Earth.
- Some construction materials, like insulation, are also dangerous to people’s health. Improper ventilation, or air movement, in homes, can lead to the spread of toxic mould. The spores of the mould enter the air in the house and make people sick.
How to reduce air pollution?
Due to the many adverse effects of pollutants in the air, people must take the necessary steps to reduce air pollution. All you need to do is make simple changes in everyday life. Some of the ways are:
Take public transportation
Instead of driving to work or school, taking public transportation reduces the number of carbon dioxide emitting vehicles on the road. An even better option is to walk or cycle to school or work. This also allows you to add some physical activity to your daily routine.
Go Local
Start travelling to shops in your local area by walking or cycling. Combine your trips if going further away. Use public transport such as bus or train and buy in bulk. It is cheaper and more convenient than driving to the store every week. Top-up necessities in between large shopping trips by purchasing items at your local businesses.
Switch energy suppliers
Consider switching energy suppliers to companies that use renewable energy sources. Begin by checking your Energy Performance Certificate. Identify places where there is room for improvement. This includes installing better insulation and more efficient appliances.
Avoid burning substances at home
Domestic burning is one of the largest contributors to particulate matter emissions. Burning solid fuels, such as open fires and wood-burning stoves can have a significant impact on air pollution. Furthermore, you should also avoid burning plant waste in your garden. Furthermore, do not use aerosol cans or smoke cigarettes.
Cut down your meat and dairy intake
Although this may not seem obvious, high meat and dairy intake lead to air pollution. This is because animal agriculture contributes to 50% of the toxic pollutants in the air. Cattle and dairy farming is responsible for large ammonia emissions, which pollute surface and groundwater along with the air.
Plant more trees and greenery
Staring your own or supporting local garden initiatives can help improve the air quality in your neighbourhood. Plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, thus, removing all CO2 from the air. Such drives are great to ensure long term health benefits to individuals. The Tree Council tells you which trees are good for your neighbourhood. You can plant those in your backyard.
Conclusion
Overall, the main cause of air pollution is rapid industrialization. With several industries coming up each year, the amount of smoke, toxic gases and particulate matter are steadily increasing. These pollutants cause several health problems, particularly respiratory disorders in humans. They can also adversely affect the environment by causing global warming, melting polar ice caps, damaging plant life etc. Thus, it is necessary for each and every one of us to take a step forward and protect the planet from destruction due to air pollution.
FAQs
1. Who is most affected by air pollution?
The groups most affected by air pollution are the elderly residents, children, people with other illnesses, people of colour and those living in poverty. Vulnerable populations like those mentioned above may experience greater negative health effects as these populations already have higher rates of heart and lung conditions
2. How to teach kids about air pollution?
Begin by explaining what air pollution is. The kid-friendly air pollution definition is as follows, “A substance that causes the air in our environment to be unhealthy”.
Then get them to read age-appropriate books on air pollution. There are plenty of books available that deal with topics from the fictional to the real world. Include these in your child’s reading list.
Indulge in activities like “Reuse and Recycle”. Make this a daily habit in your household and have your kids help create recycle bins to drop off at the local garbage station. This will teach them a small way they can help to reduce pollution in their everyday life.
Finally, encourage carpooling with friends and walks to school as much as possible. Make the ride fun by playing games with all the kids. You can do the same while walking or cycling to school. This is not only great for the environment, but also for the physical fitness of your child.
3. How to design an air pollution poster?
An air pollution poster must include captivating air pollution drawings or images depicting the problem. They add slogans like “Go green to breathe clean”, “Say no to air pollution” and “Be a part of the solution, not the problem”. Some tips are:
- Do not overcrowd the poster with images or slogans
- Ensure that the main point is clearly visible and understandable
- Use colourful images to grasp the audience’s attention


4. What to include in an essay about pollution in the air?
When writing an essay on the topic of air pollution, follow the tips given below:
- Begin with an interesting and captivating introductory paragraph about the topic. You can include the definition and outline the problem in brief.
- Avoid jargons.
- Present content in bulleted points if possible.
- Insert data, such as places or statistics wherever possible.
- Avoid writing a large monotonous block of content.
- Always conclude with an effective closing paragraph.
Use the following information to write your essay about air pollution
Air-pollution what-it-means-for-your-health | Download
Share with your friends