Grammar is an essential part of a language about which learners and teachers have differing viewpoints. The reason behind it is that your words may not convey what you have in your mind, if you do not use tenses appropriately in your sentences. Hence, it becomes more or less essential to hold or establish a firm grasp over the tenses. Some students are eager to learn or discover the correct usage of grammar, while others desire to complete grammar tasks. Some people enjoy grammar, while others find it a tedious aspect job. Whatever your point of view, you can’t avoid understanding grammar; it’s essential in every phrase you read, write, say, or hear.
The term “grammar” refers to the norms that individuals adhere to when using a language. Interestingly, it’s just the right hit if you ace the game of learning and remembering grammar rules, as it would automatically affect your fluency and confidence while conversing in the language. Here is an easy-to-follow guide on English Grammar Tenses to begin with!

- What Are Tenses?
- Did, Doing, Done!
- Present Tense
- Simple Present Tense
- How To Formulate Simple Present Tense
- Examples Of The Present Simple
- Present Continuous Tense
- How To Formulate Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- How To Formulate Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- How To Formulate The Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Tense
- Simple Past Tense
- How To Formulate The Simple Past Tense Verb
- Past Continuous Tense
- How To Formulate The Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- How To Formulate Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- How To Formulate Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Future Tense
- Simple Future Tense
- Future Continuous/Progressive Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- What is Future Perfect Progressive Tense
- Final Thoughts
- FAQ Section
What Are Tenses?
What are tenses, first and foremost?
Tenses are verbs used to indicate action and at the time when it occurs.
You’ll need to know about English tenses to figure out why the two statements are different. When something happens, the tenses tell you. Mistakes in the tense can cause confusion and misconceptions in a sentence. It may appear tough at first to master English tenses, but all you have to do is recall a few phrase forms and follow a few simple principles. Begin by breaking down the information into smaller, more easily digestible parts.
Did, Doing, Done!
In the English language, there are only three primary tenses: past, present, and future.
- The past tense is used to depict events that took place in the past.
- The present tense is used to describe current events or generic statements.
- The future tense is used to describe events that will occur at some point in the future.
Present Tense

The present tense is anything happening in current situations. Taking a closer look there are four types of present tense. These are,

- Simple present tense
- Present continuous tense
- Present perfect tense
- Finally, Present perfect continuous tense
Let’s try and understand each one more clearly!
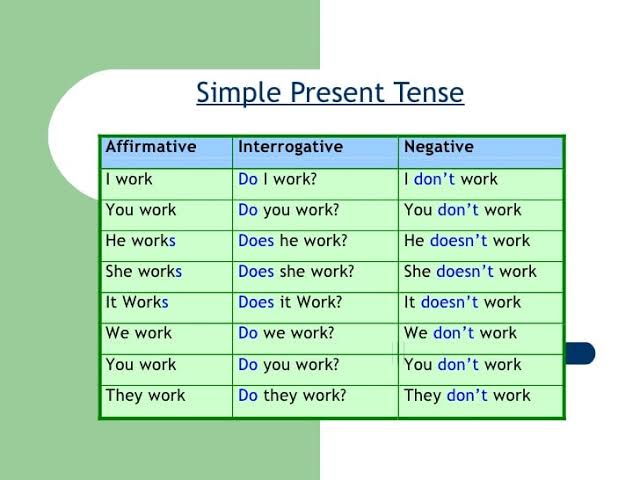
Simple Present Tense
The verb form in the simple present tense is the same as the verb’s root form. In the following situations, we employ the simple present tense:
- To demonstrate a fact or something that is consistently true
- For daily actions that we do on a regular and habitual basis
- To express one’s feelings, thoughts, opinions, and beliefs
- Planning a future action or event.
- This tense is used with few adverbs to express something that happens only once in blue moon.
- We apply it in news, reported speaking (such as sports commentary), book and story narration, and so on
How To Formulate Simple Present Tense
When the subject is singular or a singular pronoun is used, the verb is changed to the simple present tense by adding the suffix ‘-s’. For instance: travel –> travels, give –> gives, and play –> plays.
Add an ‘es’ to verbs that finish in s, ss, sh, ch, x, and o. For example: wash –> washes, mix –> mixes, go –> goes, etc.
- Change the y to an ‘i’ and add es to verbs that finish in y after a consonant (any letter that isn’t a vowel). Example, study –> studies, and fly –> flies.
Examples Of The Present Simple
- The sun sets in the west.
- This person goes to the library often.
- The Earth revolves around the Sun.
Present Continuous Tense
This tense denotes a present-tense action that is continuing. One can use the present continuous tense in the following situations:
- As previously stated, when an action is taking place at the moment of speaking.
- A future action without saying when it will take place.
- A planned or organized event or activity.
- An action or occurrence is taking place, although not always while we are speaking.
- Situation that’s continuously keeps changing.
- We employ it with adverbs like ‘always,’ which characterize an often occurring action.

How To Formulate Present Continuous Tense
It’s made up of the present participle of the verb ‘-ing’ and the present tense of the auxiliary verb ‘to be’ ( am/is/are ). As an example,
- He is reading various kinds of books.
- They are playing football now.
- She is drinking coffee.
- He is going to the library.
Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense applies in a situation of repeated activities, actions where time is irrelevant, and actions that started in the past. The only condition is that they are incomplete. The present perfect tense applies in a wide variety of situations, including:
- To describe an action that occurs in both the past and the present. Example: We have been to the museum many times.
- To define an ongoing action that began in the past and will continue in the future. Example: I have lived in South Korea since 2015.
- To describe an incomplete task. Example: It has snowed a lot this month.
- To refer to a recent action performed. Example: I have just finished my internship at a law firm.
- To characterize an action in which time was not a factor. Example: She has lost her wallet.
How To Formulate Present Perfect Tense

Depending on whether the noun being referred to is multiple or single, we must employ the simple present tense of the auxiliary verb ‘had’ or ‘has’ to construct the present perfect tense. The auxiliary verb is followed by the verb’s past participle. Have/has + past participle is another to represent it. Let’s look at a few examples.
- He have known Joey for a very long time.
- Has there ever been a pandemic during your lifetime?
- We have seen this movie already.
- The pets have made a mess in the living room.
- We have had the same house for the last 6 years.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The present perfect continuous tense is used to describe or suggest an event that is now taking place. This tense is applied in the following situations:
To describe an ongoing event that started in the past. It will continue in the future. Example: She has been working at that company for five years.
Similarly, to describe an activity or event that took place in the past but is now finished Example: She has been reading from the last night.
When the time isn’t mentioned. The tense has a broader connotation of lately without the timeframe. Example: She has been eating too much food lately.

The present perfect continuous tense has two parts:
How To Formulate The Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- ‘Have been’ or ‘has been’ is the present perfect tense of the verb ‘to be.
- Adding ‘-ing’ to the primary verb forms the present participle of the primary verb.
The following are examples of the present perfect continuous tense:
- Ritika have been shopping in that mall for three hours.
- Amal has been studying in the library for four hours.
- They have been playing outside in the rain for an hour now.
Past Tense
The past tense verb is used to express a past action, event, or state. We have four kinds of past tense verbs.
- Simple Past Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Finally, Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Simple Past Tense
The simple past tense is used to describe or express anything that occurred or existed in the past.
Describe an action, occurrence, likewise any circumstance that took place in the past.
- Characterize a behavior or occurrence of an event that occurs frequently.
- Describe a previous state of mind or a previous feeling.
- A reference to a deceased person.
- Characterize a series of events that happened quickly in the past.
- Describe an action, occurrence, likewise any circumstance that took place in the past.
- Describes an action that has been accomplished but no time has been specified.
How To Formulate The Simple Past Tense Verb
We use the suffix ‘- ed’ to produce the simple past tense verb. We append ‘-d’ and to verbs that finish in ‘e.’ Some simple past tense verbs, such as cut, put, set, and so on, do not change in the present or past tense. For instance,
- John saw a movie yesterday.
- I often brought my lunch to school.
Past Continuous Tense
The past continuous tense describes a previous event that is still happening. The past continuous tense is also used in the following situations:
- To indicate that someone is now engaged in an activity. Example: I was sleeping when he came home.
- Is used to indicate an action that occurs as a result of another action. Example: While they were painting the windows, I was painting the wall.
- For an action that was in progress when it was interrupted by another action. Example: While he was working on the project, he fell asleep.
How To Formulate The Past Continuous Tense

The past continuous tense is obtained by combining the past tense of the verb ‘ to be ‘ (was/were) with present participle verbs ending in ‘-ing’. These two tenses can be used to show that one action occurred while another was taking place. For instance:
- They were playing football in that field.
- He was reading various kinds of books.
Past Perfect Tense
In a statement or a conversation, the past perfect tense refers to an event that occurred before another event in the simple past tense. A Past Perfect Tense is used during following situations:
- To represent past before event that took place and was accomplished.
- For describing an occurrence or activity that occurred before a specific time in the past.
- To determine an action that occurred prior to another.
How To Formulate Past Perfect Tense

To form the past perfect tense, take the past tense of the verb “to have,” which is had, and moreover, combine it with the main verb’s past participle. Subject + had + past participle, for example equals past perfect tense.
- The bus had left by the time I got to the bus stop.
- They won the game because they had practiced very hard.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
This tense is used to represent events occurred in the past up until another event occurred in the past. They’re frequently employed in the following scenarios:
- For an action that took place over a long period of time and started in the past.
- To describe an action that began and ended before another event in the past.
- It’s also common in reported speech, where the present perfect continuous tense is transformed into the past perfect continuous tense.

The past perfect continuous tense, unlike the past continuous and past perfect tenses, is not employed to express state, mood, or feelings.
How To Formulate Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The past perfect tense of the verb ‘to be,’ which is ‘had been,’ and the present participle of the verb, ‘-ing,’ make this tense.
Here are some examples:
- He had been playing baseball for two hours.
- Nina had been studying since morning.
- I had been learning French for three years before I went to college.
Future Tense
The tense is used for statements that have a future connotation. In English, there is a variety of ways to refer to the future:
- Future Progressive Tense
- Simple Future Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Progressive Tense
Simple Future Tense

In basic future tense statements, both’shall’ and ‘will’ can be used, although in current English, ‘Will’ is preferred.
- It’s also used to indicate particular facts or incidents.
- It’s used to issue a warning or make an impromptu decision.
- To declare one’s readiness.
- Use the word ‘shall’ to make an offer or a recommendation
- To send someone an invitation or an order.
Here are some examples:
- I will meet him later.
- Charlie will go to the library tomorrow.
- Monica will join us in the meeting.
Future Continuous/Progressive Tense
The future continuous tense, also known as the future progressive tense, is used to describe an ongoing event in the future. It consists of two parts: a simple future form of the verb ‘to be’ + the present participle (-ing). In the following situation, there is a usage of future progressive tense:
- to broaden our horizons in the future.
- to make predictions about the future.
- Inquire or ask about upcoming events.
- To refer to future events that are ongoing or occur on a regular basis.
Here are some examples;
- We will be watching a movie premiere in this theatre on next Thursday.
- Zack will be sleeping in the afternoon.
- She will be studying at the study hall tonight.
Future Perfect Tense

In contrast to the two forms of tense stated above, the future perfect tense is a little more sophisticated. It is used to describe a task that will be done in the future.
The future perfect comprises of two parts: the simple future of the verb “to have” and the main verb’s past participle. It can be used with interrogative phrases in the affirmative and negative forms.
Here are some examples;
- Mom will have cooked our favorite meal.
- Henry will have ran by ten o’clock.
- They will have painted the windows before I have a chance to speak to them.
What is Future Perfect Progressive Tense

The tense represents an ongoing event that will end in the future. A time reference shows when the event or activity began and how long it has been going. The words like ‘since’ and ‘for’ used commonly to denote a temporal reference.
The primary verb in the present participle (base form of verb + -ing) + Auxilliary verb ‘will have been’ make up the future perfect progressive.
Here are some examples;
- We shall have been studying since Saturday.
- You will have been mingling with the pets since the morning.
- Nikita will have been taking selfies for almost 3 hours.
Final Thoughts
Some argue that grammar is no longer important, particularly in a society where texting and slangs are so in. With so many emojis, noone has time to be concerned about misplaced modifiers?
Correct grammar is a necessary skill in the professional world. It will aid you in developing more engaging job applications, proposals, articles, and novels. Furthermore, it shows that you value the English language to your viewers. Bad grammar leads to unexpected mistakes, but good grammar leads to successful communication. Its goal is to create a connection between what you’re saying and what the reader or listener understands.
Even if English isn’t your first language, clear and grammatical skills can help you ensure that others understand what you’re attempting to say or write. Since the beginning of school, we have been reading and practising the usage of tenses.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/A5uz6LWeLPM?feature=oembedHow to improve your English grammar faster!
The most significant aspect of the English language is the tenses. If you want to compose a correct phrase or convey anything to someone, you must use the correct tenses to describe your thoughts. Hence you can say that indeed Tenses are the backbone of English Literature!
Ain’t it’s always right to keep driving the fuel that can ace up your game, all just by getting your basics strong. This article attempts on doing the same. Once these rules along with the their appropriate use gets clear for you, it’s no longer a tough ride to speaking and writing correct English backed by the correct use of tenses in the sentences.
Stay On board with us and keeping coming back to our blog for more such informative articles!
FAQ Section
Why do we use present tense?
When an action is taking place right now or on a regular basis (which is why it’s also known as present indefinite), we employ the simple present tense. Using the root form or adding s or es to the end, the simple present tense is created differently depending on the person.
How are present tense and future tense different from one other?
The present tense is used to describe events that are presently taking place or that are in the process of taking place. Things that haven’t happened yet are expressed in the future tense (e.g., later, tomorrow, next week, next year, three years from now).
What is Rule of future tense?
The tense describes an activity that hasn’t happened yet but will happen after saying or in the future. Subject+ Will/ Shall + Verb is the rule (First form).
How do you use future tense?
The simple future tense can be expressed in one of two ways: “will” or “be going to.” Let’s have a look at some samples to see how they work: “Later today, I will email you some information.” “After I finish my studies, I am going to to travel more.”
What is the best way to explain past tense to a child?
Inquire about former events such as birthday celebrations, vacations, or other events from his day. Make sure he’s using the past tense while he’s doing this. If he forgets, apply the same signals as in step two and inform him that it’s something that previously happened and that we need to alter the word.
Share with your friends