Variety is just as important as quantity when it comes to vegetables and fruits in a healthy diet. One should remember that no single fruit or vegetable contains all the nutrients necessary for good health.
Fruit and vegetables should be a part of your daily routine. They’re nutritious because they’re made from natural ingredients and contain vitamins and minerals. They may also help to prevent the spread of certain diseases. There are many fruits and vegetables to choose from, as well as numerous preparation, cooking, and serving methods to pick out of. At least five servings of vegetables and two servings of fruit should be consumed each day. You can choose from a wide range of colours and varieties.
To discover what you like, you must know more about the fruits and vegetables around you! Do not worry, as Podium School has got you covered!
Key nutrients in fruits and vegetables

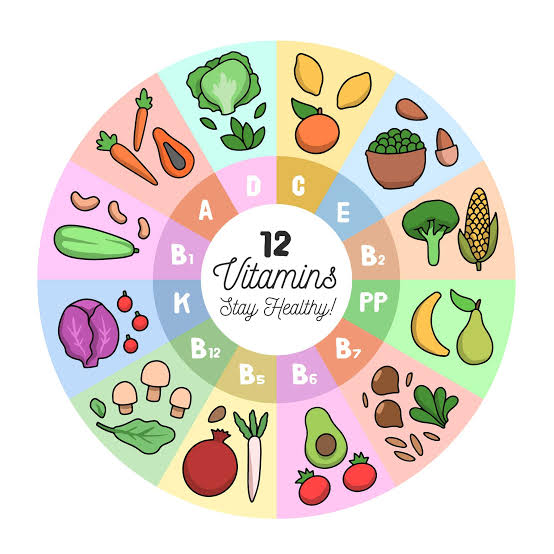
Many vitamins and minerals are found in fruits and vegetables, and they are beneficial to one’s health. Vitamins A (beta-carotene), C, and E, as well as magnesium, zinc, phosphorus, and folic acid, are all important. Homocysteine, a substance linked to coronary heart disease, may be reduced by folic acid.
Let’s explore each one briefly!
Calcium: As we all know, calcium is necessary for the maintenance of strong bones and teeth. Muscles, nerves, and some glands all require it to function properly.
Fiber: Diets high in dietary fibre have a variety of health benefits, including a lower risk of coronary heart disease.
Folate: A woman’s risk of having a child with a brain or spinal cord defect may be reduced by eating a healthy diet rich in folate.
Iron: Iron is vital for healthy blood and normal cell function.
Magnesium: Magnesium is essential for strong bones and is involved in over 300 enzymes in the human body! Muscle cramps and high blood pressure can be caused by insufficient levels.
Potassium: Diets high in potassium may help to keep blood pressure in check.
Sodium: Sodium is essential for normal cell function in the entire body. A majority of diets are high in sodium, which links to high blood pressure.
Vitamin A: Vitamin A is good for your eyes and skin, and it also protects you from infections.
Vitamin C: Vitamin C aids in the healing of cuts and wounds, as well as the maintenance of healthy teeth and gums.
Read India National Tree – Banyan!
Fruits and vegetables for good health

- Fruits and vegetables are high in dietary fibre, which can help you maintain a healthy gut and avoid constipation and other digestive problems. A high-fiber diet can also reduce your chances of developing bowel cancer.
- Heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer can all be prevented with them.
- Fruits and vegetables are the most essential parts of a healthy diet.
- Fruits and vegetables are delicious, and there is a wide range of options to choose from.
They are typically low in fat and calories as well (provided you do not fry them or roast them in lots of oil). As a result, eating them can help you maintain a healthy weight while also keeping your heart in good shape.

- Fruits and vegetables are part of a well-balanced diet that can help you lose weight or avoid weight gain because they are low in saturated fat, salt, and sugar. They can also aid in the reduction of inflammation as well as the reduction of cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
- The sodium content of fresh fruits and vegetables is very low. Many people believe celery has a high sodium content, but one stalk only has 30mg, or 1% of the daily value. Cholesterol is completely absent from fruits and vegetables.
- Phytochemicals, which are biologically active substances that can help protect against certain diseases, are found in many vegetables and fruits. You can lower your risk of type 2 diabetes, stroke, heart disease, high blood pressure, and cancer by including them in your diet. Broccoli, cabbage, collard greens, and watercress, in particular, have been linked to a lower risk of cancer.
Types of fruits
Avocado is a fruit, in case you didn’t know. We often associate fruit with sweetness and vegetables with everything else. Fruits are classified by plant classification rather than flavour.

Fruit is divided into three categories: simple, aggregate, and multiple. A majority of the fruits you’re familiar with are classified as simple fruits and fall into one of four categories. Therefore, here is a quick overlook of the different types of fruits.
| Types of fruits | Examples |
| Simple Fruit | Cherry, Plum, Apple, Citrus |
| Aggregate Fruit | Raspberry, Blackberry |
| Multiple Fruit | Pineapple, Jackfruit |
Simple fruits

A majority of the fleshy fruits you eat on a regular basis fall into this category. There are four types of fruit in the simple fruit category:
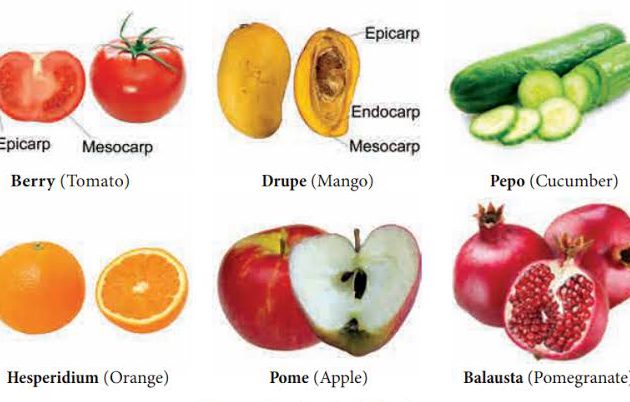
DRUPES: These fruits are also known as stone fruit because they contain a very hard seed inside the fleshy fruit (ex: cherry, plum, peach).
BERRIES: This term is a bit of a misnomer and can be confusing when it comes to berry classification. Strawberries and blackberries, for example, are not berries at all. Fruits with seeds in the centre that are usually juicy on the inside fall into this category (ex: grape, blueberry, gooseberry).
POMES: This category includes fruits that are primarily produced by trees (ex: apples, pears).
HESPERIDIUM AND PEPOS: Because of their similarities, Hesperidium and Pepos are frequently grouped together in the berries classification (ex: citrus fruits [hesperidium], watermelon [pepos]).
Aggregate fruits

These fruits are composed of a large number of drupes or berries that all come from the same flower. When you bite into a raspberry or blackberry, you’ll notice that each bulb, like a tiny cherry or plum, has a seed inside. Because of their small size, raspberries and blackberries are often referred to as druplets.
Multiple fruits

Figs, pineapples, and a variety of other fruits and vegetables fall into this category. A cluster of fruiting flowers produces multiple fruits. Each flower merges into a single mass as it matures. The mature fruit is called an infructescence, which is a fun fact!
Types of vegetables
There are numerous ways to categorise vegetables. So, depending on who you’re talking to, you’ll probably hear about different vegetable classifications, groups, and types. Thus, vegetables are usually classified into eight categories based on the parts that are edible.
| Vegetable type | Example |
| Flower Vegetables | cauliflower, broccoli, artichoke, caper, and loroco |
| Leafy Vegetables | Spinach, cabbage, lettuce, bok choy, Brussels sprouts, kale, chard, and watercress |
| Tuber Vegetables | Potato, cassava, sweet potato, kumara, yam, taro, Jerusalem artichoke, and ulluco |
| Root vegetables | Carrots, radish, turnip, beet, horseradish, celery, turmeric, and parsnips |
| Bulb Vegetable | Onion, shallot, garlic, leek, spring onion, scallion, and fennel |
| Stem Vegetable | Asparagus, celery, chard, fennel, fiddlehead, cardoon, and bamboo shoots. |
| Fruit Vegetables | Squash, avocado, bitter melon, and bell pepper. |
| Pods and Seed Vegetables | Peas, beans, lentils, okra, chickpea, peanut, soybean, and licorice |
Flower vegetables

Plants that produce edible flowers are known as flower vegetables. Flower vegetables are mostly grown for their flower buds and are only available during specific seasons. The most commonly eaten vegetable flowers include cauliflower, broccoli, artichoke, caper, and loroco.
Leafy vegetables
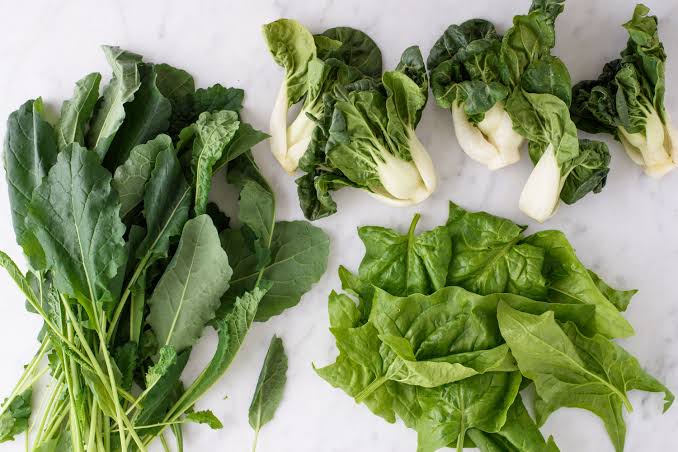

Leafy vegetables, also known as greens, salad greens, or vegetable greens, are high in vitamins and minerals. They’re grown primarily for their leafy parts, which can be eaten raw or cooked. Spinach, cabbage, lettuce, bok choy, brussels sprouts, kale, chard, and watercress are some of the best examples of leafy vegetables.
Tuber vegetables
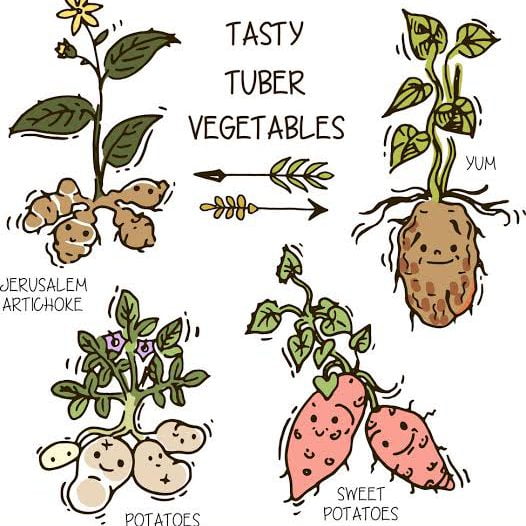
Tuber vegetables are vegetables that grow underground on the root of a plant. Tuberous vegetables are high in starch and are a staple food in many cultures. Potato, cassava, sweet potato, kumara, yam, taro, Jerusalem artichoke, and ulluco are the most popular tuber vegetables.
Root vegetables
Root vegetables are vegetables that grow underground and produce edible roots. These vegetables are high in nutrients and also contain carbohydrates, starches, and sugar. A root vegetable can have a round or long shape, as well as a fleshy texture, depending on the type. The most commonly consumed root vegetables are carrots, radish, turnip, beet, horseradish, celery, turmeric, and parsnips.
Bulb vegetables

Bulb vegetables are plants that grow only a few inches below the ground and produce edible bulbs. These are usually thick and aromatic, and depending on the type, they can be eaten raw or added to cooked dishes. Onion, shallot, garlic, leek, spring onion, scallion, and fennel are just a few of the most popular bulbs.
Stem Vegetables
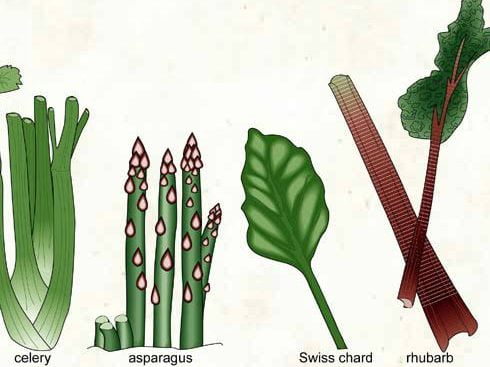
Stem vegetables are plants that are edible and grow above ground. Corms, rhizomes, and tubers, for example, are modified stems that grow above and below ground. The most commonly used stem vegetables include asparagus, celery, chard, fennel, fiddlehead, cardoon, and bamboo shoots.
Fruit vegetables
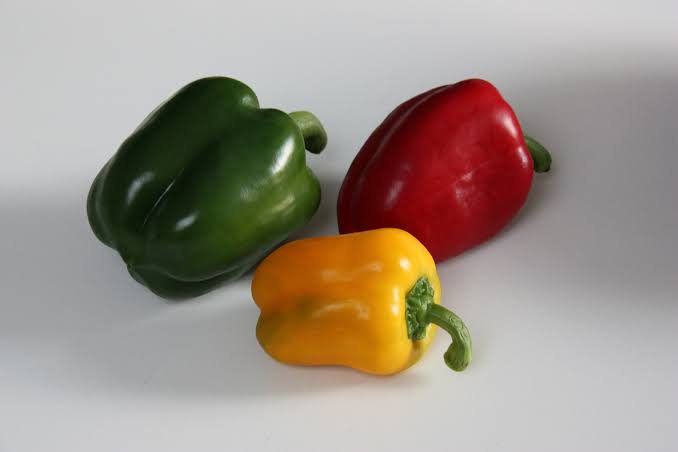

Fruit vegetables are plants that are botanically classified as fruits but are used in the kitchen as vegetables. It may surprise you to learn that some fruits are actually vegetables and vice versa. Tomatoes, cucumbers, and eggplants are among the most popular and widely consumed fruits and vegetables. Fruit vegetables include squash, avocado, bitter melon, and bell pepper.
Pods and seed vegetables

Podded vegetables, also known as legumes, are vegetables that have seeds enclosed in a pod. These vegetables are high in protein and fibre, and they also contain important minerals. Peas, beans, lentils, okra, chickpea, peanut, soybean, and licorice are the most popular podded vegetables.
Colours of fruits and vegetables
The most health benefits and disease protection come from eating a wide variety of fruits and vegetables. Protective compounds are found in foods that are similar in colour. To get the full range of health benefits, try to eat a rainbow of colourful fruits and vegetables every day. Consider the following scenario:
Tomatoes and watermelon are examples of red foods. These have lycopene in them, which is thought to be beneficial in the fight against prostate cancer and heart disease.

Spinach and kale are examples of green vegetables. These are high in lutein and zeaxanthin, which may help prevent macular degeneration as people age.

Blue and purple fruits and vegetables, such as blueberries and eggplant These contain anthocyanins, which may aid in cancer prevention.

Cauliflower, for example, is a white food. These contain sulforaphane, which may help prevent cancer in some people.

Which fruits and vegetables are best?
They’re all fantastic! You’ll get all the different types of nutrients you need if you eat a variety of fruits and vegetables. To get to the recommended 4 ½ cups of fruits and vegetables per day, the American Heart Association recommends filling at least half of your plate with them. The good news is that all produce counts, so canned, fresh, and frozen fruits and vegetables can all help you reach your goal.
When purchasing canned, dried, or frozen vegetables and fruit, compare food labels to find the products with the least sodium and added sugars.
Breakfast
- Fruit such as melon, grapefruit, or other fruits can be consumed.
- Toss your cereal with bananas, raisins, or berries.
- Drink a small glass of juice (6 ounces). Check to see if it’s 100% fruit or vegetable juice with no added sugar or sodium – not a “fruit drink,” “cocktail,” or “punch.”
- Vegetables, chopped, can be added to eggs or potatoes. Onions, celery, green or red bell peppers, or spinach are all good options.
Lunch
- Lunch should include a fruit or vegetable salad.
- Cucumber, sprouts, tomato, lettuce, or avocado are good additions to your sandwich.
- Serve yourself a bowl of vegetable soup (Compare food labels and choose the lowest-sodium item in your store, or make soup from scratch.)
- Instead of chips, eat a piece of fruit or raw veggie sticks.
Snacks
- Keep green or red bell peppers, green beans, celery, or carrots on hand as raw veggie sticks.
- In your purse or pocket, keep dried fruit like raisins, dates, or dried apricots.
- Fresh fruit of any kind is welcome, including grapes, apples, bananas, oranges, kiwis, and other tropical fruits.
- A bowl of frozen fruits or vegetables, such as grapes, peas, or bananas, is a refreshing treat on hot days.
Dinner
- Dinner should include a fruit or vegetable salad.
- Serve with a side of steamed or microwaved vegetables – frozen vegetables are acceptable!
- Put a whole potato, sweet potato, or yam in the oven with your meal when it’s cooking.
- When making soup, stew, beans, rice, spaghetti sauce, and other sauces, add chopped vegetables like onions, garlic, and celery.
- For the last three minutes of cooking, add frozen peas to the rice.
Preparation and cooking of fruits and vegetables
Although some vegetables are eaten raw, most are cooked. Some nutrients and phytochemicals in plant foods are damaged by cooking and processing.

The following are some suggestions for getting the most out of your fruits and vegetables:
- If at all possible, consume raw fruits and vegetables.
- Smoothies made with pureed fruits or vegetables are an excellent choice.
- Use a sharp knife to avoid bruising when cutting fresh fruits.
- Remove only the inedible parts of the vegetables; the best nutrients are sometimes found in the skin, just beneath the skin, or in the leaves.
- Stir-fry, grill, microwave, bake, or steam with nonstick cookware and mono-unsaturated oils.
- To avoid nutrient loss, don’t overcook.
- Instead of sour cream, butter, and creamy sauces, use vegetable pestos, salsas, chutneys, and vinegars.
Cooked food may actually increase some nutrients, such as carotenoids. Cooked tomatoes, for example, have higher levels of carotenoids, particularly lycopene, which is yet another reason to prepare fruits and vegetables in a variety of ways.
After you’ve prepared and cooked your vegetables and fruit, spend some time on the presentation. People are more likely to enjoy a meal if it has a wide variety of flavours and is visually appealing in addition to being tasty. Sit at the table and savour your meal without being distracted by the television.
Read Continents and Oceans of the World
Tips to eat more fruits and vegetables each day
Keep fruit out in the open where you can see it. To satisfy a sweet tooth, place several washed and ready-to-eat whole fruits in a bowl or store chopped colourful fruits in a glass bowl in the refrigerator.
Choose something different from the grocery. A healthy diet emphasises variety and colour. Try to include at least one serving from each of the following categories on most days: Fruits and vegetables that are dark green in colour; fruits and vegetables that are yellow or orange in colour; fruits and vegetables that are red in colour; legumes (beans and peas); and citrus fruits.
Make a meal out of it. Cooking new recipes with more vegetables is a good idea. Salads, soups, and stir-fries are just a few ways to incorporate more vegetables into your diet.
Begin with a good meal. It’s important to start as you mean to go on if you want to cram more portions into your day. Savoury breakfasts can include grilled tomatoes, mushrooms, or beans, as well as dried and fresh fruit.
Finally, there are Smoothies! All you need is fruit and ice if you have a blender to make a delicious smoothie with all of your favourite flavours. And here’s a hint: when making a fruit smoothie, you can add as much fresh spinach as you want. It is not until you cook spinach that it begins to taste like spinach. Even children are unable to distinguish between the two!
Final thoughts
If you already consume a variety of fruits and vegetables on a daily basis, you may be ready to take the next step: adding colour to your diet. Vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients found in fruits and vegetables may help to prevent heart disease, cancer, and other illnesses. Fibre, potassium, folate, and vitamins A and C are among these nutrients. Eating a variety of coloured fruits and vegetables is the best way to get all of the nutrients.
The stomach capacities of children are smaller, and their energy requirements are higher than those of adults. They are unable to consume the same portion sizes as adults. You should, however, encourage your children to consume a wide variety of fruits and vegetables.
Your children will have the energy they require to play, concentrate better, learn, sleep better, and develop stronger teeth and bones if they eat well. Building good habits in their early years can help them maintain a healthy diet for the rest of their lives.
Here are a few simple ways to serve fruits and vegetables:
- fruit and vegetable salads
- vegetable or meat-and-vegetable stir-fries
- raw fruit and vegetables
- vegetable soups
- snack pack, stewed or canned fruits or dried fruits.
Fruit juice should be consumed in moderation because it lacks the nutrients that fresh fruit provides. It also has high sugar content. These sugars, despite being ‘natural,’ are not necessarily good for your health. Instead, hydrate yourself with water and eat some fruit.
Know your Fruits and Veggies – Download
FAQ Section
What fruits and vegetables are good for you and why?
Blueberries, bananas, avocados, and citrus fruits are among the healthiest fruits. Kale, spinach, carrots, and sweet potatoes are among the healthiest vegetables. Vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals abound in fruits and vegetables, making them nutritious.
What are fruits good for?
Fruits are high in fibre and are a good source of essential vitamins and minerals. Fruits also contain a variety of antioxidants that are good for your health, such as flavonoids. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help reduce the risk of heart disease, cancer, inflammation, and diabetes.
Is it good to eat fruits and vegetables every day?
Fruit and vegetables should be a staple in your diet. They’re healthy because they’re natural and contain vitamins and minerals. They may also aid in the prevention of certain illnesses. There are numerous fruits and vegetables to choose from, as well as numerous ways to prepare, cook, and serve them. Each day, you should consume at least five servings of vegetables and two servings of fruit. Choose from a variety of colours and varieties.
Is watermelon good for you?
It contains a lot of water and nutrients like lycopene, citrulline, and vitamins A and C. More research is needed, but studies suggest that this sweet, red melon may improve heart health, reduce muscle soreness, and reduce inflammation.
Which vegetable is the queen of vegetables?
Broccoli is a hearty, tasty vegetable that is high in a variety of nutrients. It is said to be the most nutritionally dense vegetable on the planet. Broccoli is one of the first vegetables that come to mind when we think of green vegetables to include in our diet. Broccoli is a type of edible green plant that belongs to the cabbage family.
Share with your friends





