A phobia is a form of anxiety disorder. It can cause a person to have excessive or incapacitating fear of a situation or item that does not normally cause any genuine harm. This article defines phobias as well as discusses the many types of phobias. It also contains a list of some of the most frequent or common phobias and some treatment options.
What exactly is a phobia?
A phobia is an intense or incapacitating dread of something that provides no genuine harm. However, if the item does represent a threat, the person’s reaction is frequently out of proportion to the actual threat. People who suffer from a phobia are usually aware that their dread is unjustified. Regardless, when they are exposed to their fear, they suffer intense anxiety.
Each individual’s phobia differs in intensity. Some people are able to avoid the issue while experiencing just minimal anxiety as a result of their phobia. On the other hand, others experience full-fledged panic attacks with all of the accompanying incapacitating symptoms. These people frequently complain of dizziness, loss of bladder or bowel control, tachypnea, discomfort, as well as shortness of breath.
Types of Phobias
According to the fifth edition of The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), phobias are of three types- specific phobias, social phobias, and agoraphobia.
Specific Phobias
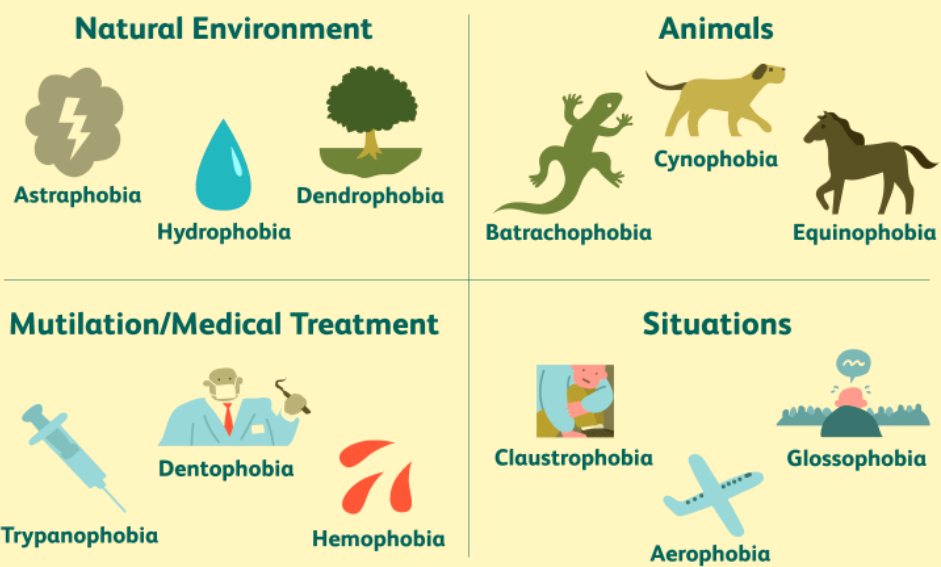
Specific, or “simple,” phobias are those that are associated with a specific object or scenario. The DSM-5 Trusted Source categorizes this set of phobias as follows:
- Animal phobia: For example, a fear of dogs, snakes, and spiders.
- Natural environment phobias: For example, a fear of storms, water, and heights.
- Blood, injection, and injury phobias: For example, a fear of needles, invasive medical procedures, and blood.
- Situational phobia: For example, a fear of flying and enclosed areas.
- Other phobias: Any phobia that does not fall into one of the preceding categories.
When people are young, they tend to develop specific phobias. However, in many cases, the intensity of these phobias lessens with maturity.
Social Phobia or Social Anxiety
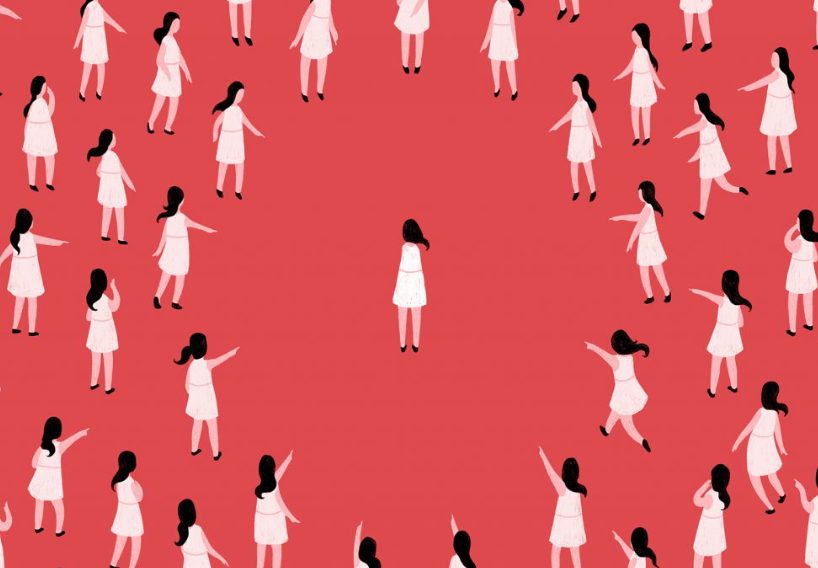

A social phobia refers to intense anxiety that being in social situations might result in embarrassment or disgrace. Fear of public speaking is an example of social phobia.
Agoraphobia

This term refers to the dread of being in public places or crowded places when there is no simple way out. People suffering from agoraphobia may become housebound in extreme situations because they are scared to leave their safe area.
Because the place or item that produces the fear is far more difficult to avoid, social phobias and agoraphobia are more likely to cause life impairment.
Common Phobias
There are around 400 different types of phobias. Here, we have listed some of the most common phobias faced by people.
Arachnophobia
Perhaps the most well-known of all phobias is arachnophobia. It refers to an aversion to spiders, often known as arachnids. According to estimates, one in every three women and one in every four males suffer from arachnophobia.
Ophidiophobia
This refers to the fear of snakes. This phobia, like arachnophobia, has its origins in human evolution. Personal encounters with snakes and cultural influences might also play a role.
Acrophobia
Over 20 million individuals suffer from acrophobia or a fear of heights. This phobia, in particular, is commonly linked to anxiety episodes and avoidance of the trigger, high areas, in this situation.
Aerophobia
This term refers to a fear of flying. It affects an estimated 8 million individuals. Aerophobia can be especially difficult to avoid in today’s world of travel and transportation, but it can be handled with strategies such as exposure treatment.
Cynophobia
Fear of dogs, often known as cynophobia, is one of the most widely treated phobias. In fact, cynophobia affects 36% of all individuals seeking phobia therapy. In most situations, this phobia occurs because of a terrible incident in the patient’s history.
Claustrophobia
When the fear of enclosed places (claustrophobia) interferes with a person’s capacity to perform at work, school, or other everyday activities, it becomes a phobia. Tunnels, elevators, trains, as well as aircraft, are all common triggers.
Trypanophobia
This term refers to an irrational dread of injections. People who have trypanophobia suffer intense anxiety while undergoing treatments that require a needle, such as getting an injection or while nurses collect their blood. Furthermore, they frequently get disoriented or faint at the sight of a needle.
The Treatments Available to Treat a Phobia
Typically, the treatment of phobias involves counseling, medication, or a combination of the two. The different treatment options for phobias are as follows:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy, or CBT, helps an individual manage their phobias by gradually changing the way they think. It is founded on principles of the interdependence of ideas, beliefs, feelings, as well as behaviors. A patient may require multiple CBT sessions to break the cycle of negative thoughts that lead to phobias.
Exposure Therapy
This is a type of therapy that involves exposing oneself to the object that triggers anxiety. Through this therapy, the affected individual can desensitize themselves to the item or circumstance.
Anxiety-relieving Drugs
The doctor may prescribe some anxiety-relieving drugs in order to benefit from exposure treatment. While these drugs aren’t a cure for phobias, they can make exposure therapy less painful.
Other Medications
To alleviate anxiety or panic, the doctor may also prescribe beta-blockers and benzodiazepines.
Summing It Up!
A phobia is an intense or incapacitating fear of a certain circumstance or item that is unlikely to offer any genuine risk. Some triggers are more difficult to avoid than others. If a person’s phobia creates continual worry or interferes with their everyday life, they should seek professional therapy. A person can seek assistance from a doctor or a psychotherapist on how to obtain these therapies.
Share with your friends